Unveiling the Economic Landscape: A Deep Dive into Chicago’s Income Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Economic Landscape: A Deep Dive into Chicago’s Income Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Economic Landscape: A Deep Dive into Chicago’s Income Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Economic Landscape: A Deep Dive into Chicago’s Income Map

Chicago, a vibrant metropolis known for its rich history, diverse culture, and thriving economy, is also a city marked by significant income disparities. Understanding these disparities is crucial for policymakers, community leaders, and residents alike, as it sheds light on the challenges and opportunities facing different neighborhoods and communities.
This comprehensive analysis explores the intricate tapestry of Chicago’s income landscape, examining the underlying factors shaping income distribution and the implications for the city’s social and economic well-being. Through the lens of a detailed income map, we delve into the nuances of income inequality, highlighting both the areas of prosperity and those facing economic hardship.
Decoding the Data: Understanding the Chicago Income Map
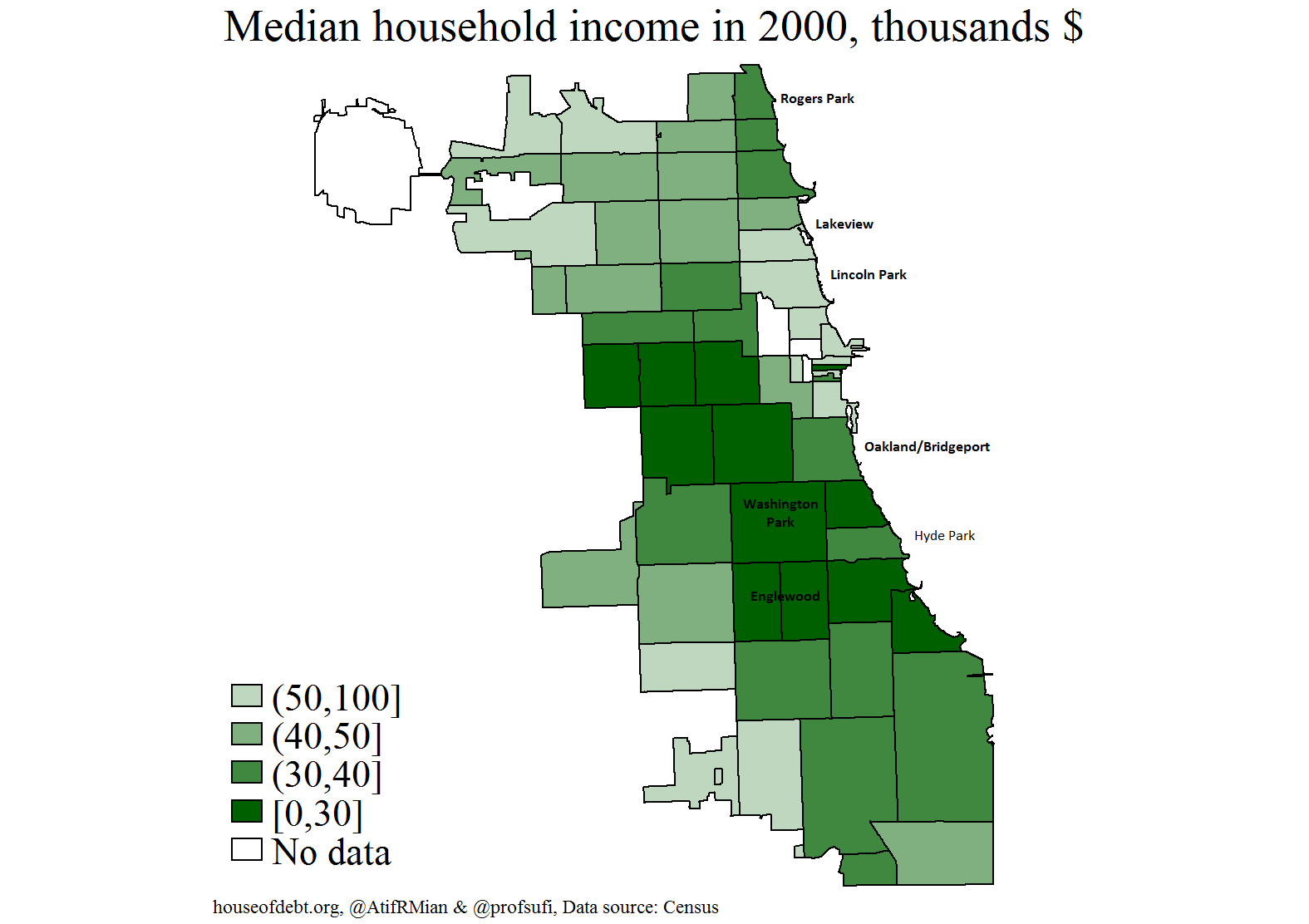
The Chicago income map is a visual representation of income levels across different neighborhoods, providing a powerful tool for understanding the city’s economic landscape. It typically depicts income data by census tract, a geographic unit encompassing a relatively small population, allowing for a granular view of income distribution.
The map utilizes color gradients or symbols to represent income levels, with higher income areas often depicted in warmer colors, while lower income areas are represented by cooler colors. This visual representation allows for quick identification of areas with high, medium, and low income levels, revealing patterns and trends that might not be immediately apparent from raw data alone.
Key Insights from the Chicago Income Map
Analyzing the Chicago income map reveals several key insights about the city’s economic landscape:
- Geographic Concentration of Income: The map clearly demonstrates that income levels are not evenly distributed across Chicago. Certain neighborhoods consistently exhibit higher income levels, often clustered in central areas and affluent suburbs, while other neighborhoods, particularly those on the city’s south and west sides, tend to have lower income levels.
- Spatial Correlation with Other Socioeconomic Factors: Income disparities often correlate with other socioeconomic factors, such as education levels, employment rates, and access to quality healthcare. Neighborhoods with higher income levels tend to have higher educational attainment, lower unemployment rates, and better access to healthcare facilities.
- Historical and Structural Factors: The current income distribution in Chicago is influenced by a complex interplay of historical and structural factors, including discriminatory housing policies, segregation, and economic disinvestment in certain neighborhoods. These factors have contributed to persistent income inequalities, creating challenges for residents in lower income areas.
Beyond the Map: Exploring the Dynamics of Income Inequality
While the income map provides a valuable visual representation, it is crucial to understand the factors driving income disparities. A deeper analysis reveals the following key drivers:
- Employment Opportunities and Wages: Access to well-paying jobs is a significant factor influencing income levels. Neighborhoods with higher concentrations of high-paying industries tend to have higher average incomes. Conversely, areas with limited job opportunities or a predominance of low-wage jobs often face income challenges.
- Education and Skills: Education and skills are essential for securing high-paying jobs. Neighborhoods with higher educational attainment and access to quality education often have higher income levels. Conversely, areas with limited educational opportunities and lower educational attainment tend to have lower average incomes.
- Housing Costs and Affordability: High housing costs can significantly impact income levels, particularly for lower-income households. In areas with high housing costs, a larger portion of income is often spent on housing, leaving less disposable income for other needs.
- Access to Healthcare and Social Services: Access to quality healthcare and social services is crucial for individual and community well-being. Neighborhoods with limited access to healthcare and social services often face higher healthcare costs and lower overall well-being, contributing to income disparities.
The Importance of Addressing Income Inequality
Addressing income inequality is not only a matter of social justice but also a critical factor for the overall economic well-being of Chicago. Here’s why:
- Economic Growth and Prosperity: Income inequality can hinder economic growth by limiting consumer spending and investment. When a significant portion of the population has limited disposable income, it can dampen overall economic activity.
- Social Cohesion and Stability: Income inequality can contribute to social unrest and instability. When there is a wide gap between the wealthy and the poor, it can lead to feelings of resentment, frustration, and a breakdown of social trust.
- Health and Well-being: Income inequality has a direct impact on health and well-being. Lower-income individuals and communities often experience higher rates of chronic diseases, shorter life expectancies, and reduced access to quality healthcare.
Addressing Income Inequality: A Multifaceted Approach
Addressing income inequality requires a multifaceted approach that tackles the root causes of the problem. Key strategies include:
- Investing in Education and Skills Development: Expanding access to quality education and training programs can equip individuals with the skills needed to secure higher-paying jobs.
- Promoting Economic Development in Disadvantaged Neighborhoods: Investing in infrastructure, supporting small businesses, and creating job opportunities in lower-income areas can help boost economic activity and raise income levels.
- Addressing Housing Affordability: Implementing policies to increase affordable housing options, regulate rent increases, and address discriminatory housing practices can help ensure that housing costs are not a barrier to economic mobility.
- Expanding Access to Healthcare and Social Services: Providing access to quality healthcare, childcare, and other essential social services can improve overall well-being and reduce financial burdens on lower-income families.
FAQs about the Chicago Income Map
Q: What is the purpose of the Chicago income map?
A: The Chicago income map serves as a visual tool for understanding income distribution across different neighborhoods, highlighting areas of prosperity and those facing economic hardship. It helps policymakers, community leaders, and residents gain insights into the city’s economic landscape and the factors contributing to income inequality.
Q: How is the Chicago income map created?
A: The map is typically created using income data from the U.S. Census Bureau, which collects detailed information on income levels by census tract. This data is then visualized using color gradients or symbols to represent income levels, allowing for a clear representation of income distribution across different neighborhoods.
Q: What are some of the limitations of the Chicago income map?
A: The map provides a snapshot of income levels at a specific point in time, but it does not capture the dynamic nature of income inequality. Additionally, it does not account for individual income variations within a census tract, which can be significant.
Q: What are some of the key insights that can be derived from the Chicago income map?
A: The map reveals the geographic concentration of income, highlighting areas with higher and lower income levels. It also demonstrates the spatial correlation between income and other socioeconomic factors, such as education levels, employment rates, and access to healthcare.
Q: How can the Chicago income map be used to address income inequality?
A: The map can be used to identify areas with high concentrations of poverty and to target interventions to address the underlying causes of income inequality. It can also inform policy decisions related to economic development, housing affordability, and access to healthcare and social services.
Tips for Interpreting the Chicago Income Map
- Consider the data source and methodology: The map is only as accurate as the data used to create it. Understand the data source and methodology to ensure the map accurately reflects income levels.
- Look for patterns and trends: Analyze the map to identify areas with high, medium, and low income levels and look for patterns or trends that might indicate underlying factors contributing to income inequality.
- Compare data across time: Examine income maps from different time periods to understand how income distribution has changed over time and identify areas where income inequality is increasing or decreasing.
- Consider context: The map is a valuable tool, but it is essential to consider the context surrounding income inequality. Factors such as housing costs, employment opportunities, and access to education and healthcare can significantly impact income levels.
Conclusion
The Chicago income map serves as a powerful tool for understanding the city’s economic landscape and the challenges and opportunities facing different neighborhoods. By providing a visual representation of income distribution, the map highlights the stark realities of income inequality and the need for comprehensive strategies to address this issue.
Addressing income inequality requires a multifaceted approach that tackles the root causes of the problem, including investing in education and skills development, promoting economic development in disadvantaged neighborhoods, addressing housing affordability, and expanding access to healthcare and social services. By understanding the dynamics of income inequality and implementing targeted interventions, Chicago can work towards creating a more equitable and prosperous future for all its residents.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Economic Landscape: A Deep Dive into Chicago’s Income Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!