Unveiling the Earth’s Cracks: A Comprehensive Guide to Fissure Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Earth’s Cracks: A Comprehensive Guide to Fissure Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Earth’s Cracks: A Comprehensive Guide to Fissure Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Earth’s Cracks: A Comprehensive Guide to Fissure Maps
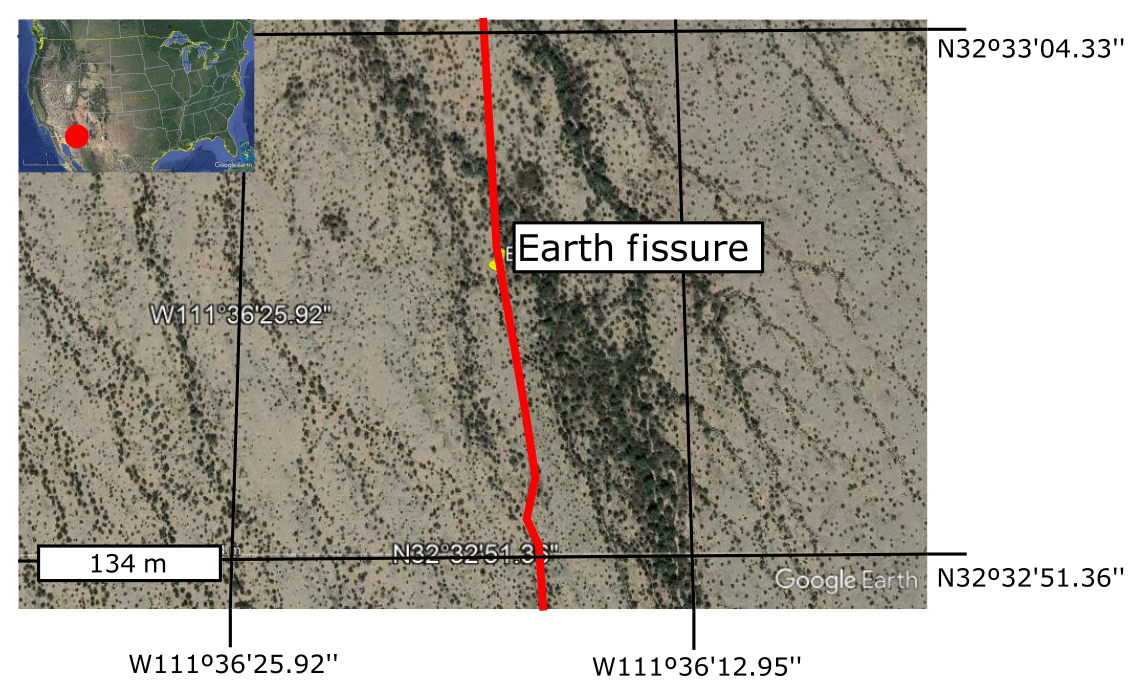
The Earth’s surface, seemingly solid and stable, is in constant flux. Beneath the familiar landscapes, a dynamic network of fractures and fissures crisscrosses the planet, revealing the hidden forces that shape our world. These cracks, often invisible to the naked eye, hold invaluable information about geological processes, environmental hazards, and even the potential for resource extraction. Understanding these fissures, their formation, and their implications is crucial for a wide range of disciplines, from geology and seismology to environmental science and engineering.
Understanding Fissure Maps: A Window into Earth’s Dynamics
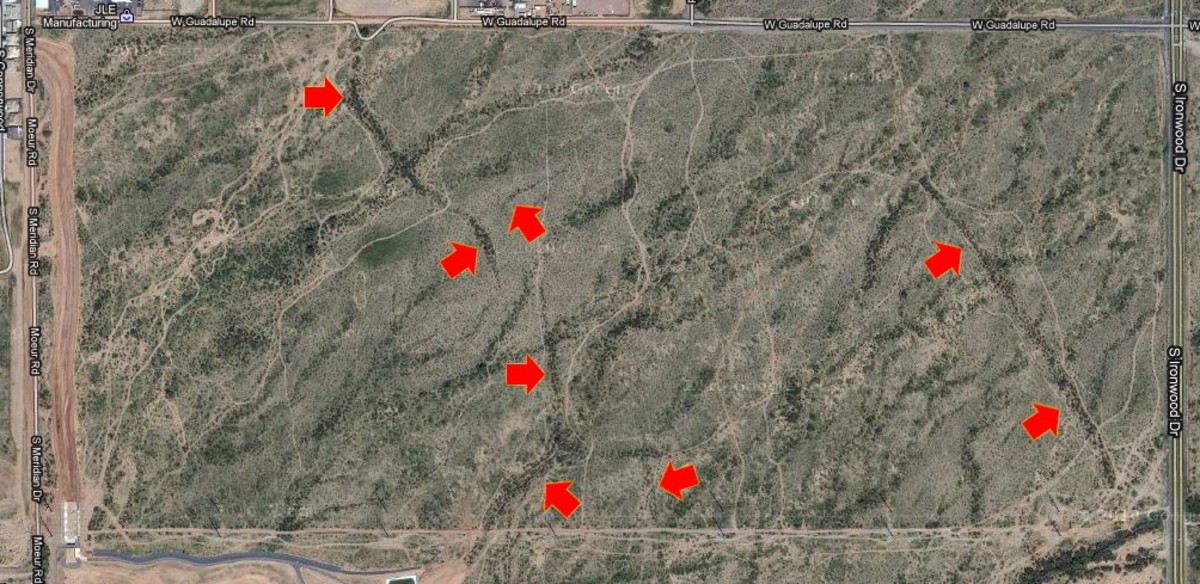
Fissure maps, as the name suggests, are graphical representations of these fractures. They depict the location, orientation, size, and other characteristics of fissures across a specific area, be it a region, a continent, or even the entire globe. These maps serve as a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing the complex interplay of geological forces that shape the Earth’s crust.
The Genesis of Fissures: A Tale of Tectonic Forces and Beyond
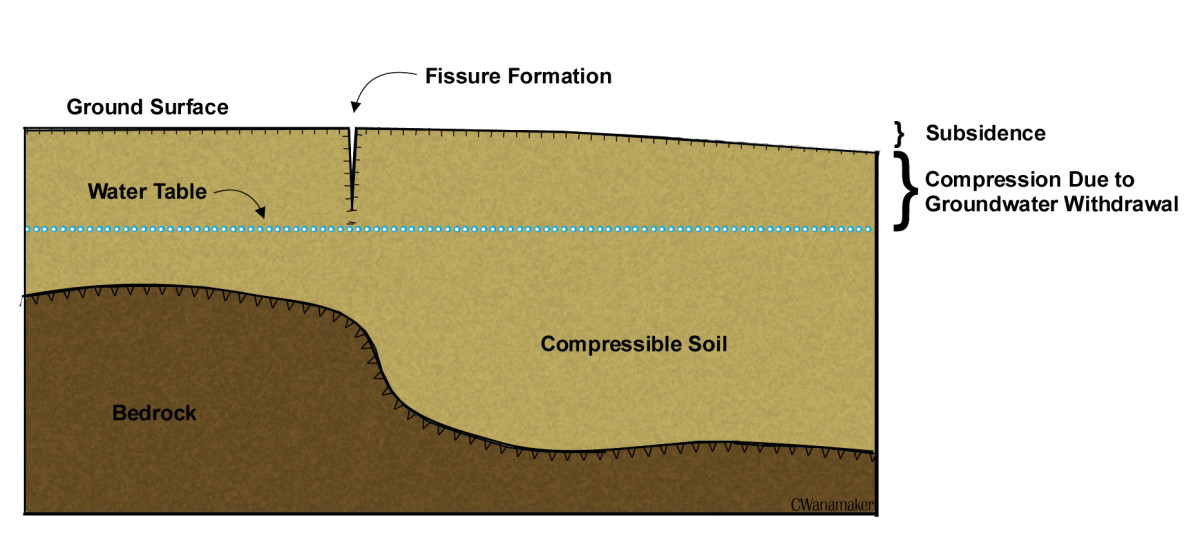
Fissures are primarily formed by tectonic forces, the slow but relentless movement of the Earth’s lithospheric plates. As these plates collide, separate, or slide past each other, they exert immense pressure on the surrounding rock, leading to the formation of fractures. These fractures can range in size from microscopic cracks to massive faults that extend for hundreds of kilometers.
Beyond tectonic forces, other factors contribute to fissure formation:
- Volcanic Activity: The eruption of magma from beneath the Earth’s surface can create extensive fissures, often accompanied by volcanic ash and lava flows.
- Erosion and Weathering: Over time, the relentless forces of wind, water, and ice can erode and weather rock, creating fissures and cracks.
- Human Activity: Mining, drilling, and other human activities can induce stress on the Earth’s crust, leading to the formation of fissures.
The Significance of Fissure Maps: Applications Across Disciplines
The importance of fissure maps extends far beyond the realm of pure scientific inquiry. These maps serve as vital tools for a diverse range of applications, including:
- Geological Exploration: Fissure maps aid in identifying potential areas for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration. They reveal pathways for the migration of underground fluids and provide insights into the structural integrity of the Earth’s crust.
- Seismological Studies: Fissures often act as pathways for the propagation of seismic waves, making them crucial for understanding earthquake hazards. Fissure maps can help pinpoint areas prone to seismic activity and inform earthquake-resistant building design.
- Environmental Monitoring: Fissures can act as conduits for groundwater flow, impacting water quality and availability. Fissure maps assist in identifying areas susceptible to groundwater contamination and inform sustainable water management practices.
- Geotechnical Engineering: Fissures can significantly impact the stability of infrastructure, particularly in areas prone to seismic activity or landslides. Fissure maps aid in designing structures that can withstand the stresses imposed by these geological features.
Decoding the Language of Fissures: Understanding Key Parameters
Fissure maps are not simply a collection of lines on a map. They are rich in information, revealing crucial details about the geological processes that shaped the Earth’s surface. Key parameters depicted on these maps include:
- Location: The geographical coordinates of each fissure are essential for mapping their distribution and understanding their spatial relationships.
- Orientation: The direction of a fissure, expressed as an azimuth angle, provides insights into the stresses that caused its formation.
- Length and Width: These dimensions reveal the scale of the fissure and its potential impact on the surrounding environment.
- Depth: The depth of a fissure is critical for understanding its influence on groundwater flow and its potential for triggering landslides.
- Density: The number of fissures per unit area, referred to as fissure density, provides insights into the degree of fracturing in a region.
Fissure Mapping Techniques: Unveiling the Hidden Cracks
The creation of fissure maps involves a combination of field observations, remote sensing techniques, and sophisticated data analysis.
- Field Surveys: Geologists and engineers conduct field surveys to identify and characterize fissures using visual inspection, ground penetrating radar (GPR), and other geophysical methods.
- Remote Sensing: Aerial photography, satellite imagery, and LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) provide high-resolution views of the Earth’s surface, enabling the identification of fissures from afar.
- Data Analysis: The data collected from field surveys and remote sensing is analyzed using specialized software to create detailed fissure maps.
FAQs about Fissure Maps: Addressing Common Questions
Q: What is the difference between a fissure and a fault?
A: While both are fractures in the Earth’s crust, faults are larger and more significant. Faults typically involve a displacement of rock masses along the fracture, while fissures are generally smaller and may not involve significant displacement.
Q: How are fissure maps used to predict earthquakes?
A: While fissure maps cannot directly predict earthquakes, they provide valuable information about the distribution of faults and the potential for seismic activity. By analyzing the density and orientation of fissures, seismologists can identify areas prone to earthquakes.
Q: Can fissure maps be used to predict volcanic eruptions?
A: Fissure maps can provide insights into the location of volcanic vents and the pathways of magma flow. However, predicting volcanic eruptions requires a multidisciplinary approach that considers various factors, including seismic activity, gas emissions, and ground deformation.
Q: How do fissure maps contribute to sustainable development?
A: Fissure maps are crucial for sustainable resource management. They help identify areas suitable for resource extraction, minimize environmental damage, and ensure the long-term viability of development projects.
Tips for Utilizing Fissure Maps: Maximizing Their Potential
- Consult with experts: When interpreting fissure maps, it is essential to consult with experienced geologists or geotechnical engineers who can provide valuable insights into the specific context of the map.
- Consider the scale: Fissure maps can be created at various scales, from local to global. Choose a map appropriate for the specific application and area of interest.
- Integrate with other data: Fissure maps are most effective when integrated with other geological, environmental, and engineering data. This approach provides a comprehensive understanding of the complex factors influencing a given area.
- Stay updated: Geological processes are constantly evolving, and new information is constantly being gathered. Regularly update fissure maps with the latest data to ensure accurate and relevant information.
Conclusion: Fissure Maps – A Key to Understanding Earth’s Dynamics
Fissure maps, though often overlooked, provide a vital window into the dynamic processes shaping our planet. They offer a wealth of information about the Earth’s crust, its vulnerabilities, and its potential for resource extraction. By understanding the language of fissures, we gain valuable insights into geological hazards, environmental challenges, and the potential for sustainable development. As our understanding of the Earth’s dynamics continues to evolve, fissure maps will play an increasingly crucial role in guiding our decisions and shaping our future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Earth’s Cracks: A Comprehensive Guide to Fissure Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!