Unlocking The Secrets Of Washington’s Precipitation: A Comprehensive Guide To The State’s Rainfall Patterns
Unlocking the Secrets of Washington’s Precipitation: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Rainfall Patterns
Related Articles: Unlocking the Secrets of Washington’s Precipitation: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Rainfall Patterns
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Secrets of Washington’s Precipitation: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Rainfall Patterns. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Secrets of Washington’s Precipitation: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Rainfall Patterns

Washington state, known for its lush landscapes and diverse ecosystems, experiences a wide range of precipitation patterns. Understanding these patterns is crucial for various sectors, including agriculture, water management, and even tourism. This article delves into the intricate world of Washington’s precipitation, exploring its geographical variations, seasonal trends, and the factors influencing rainfall distribution across the state.
A State Divided: Exploring Geographical Precipitation Variations
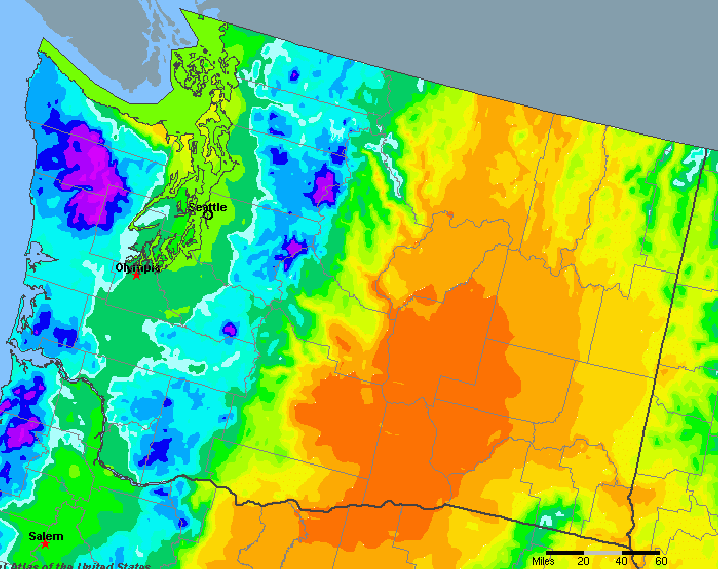
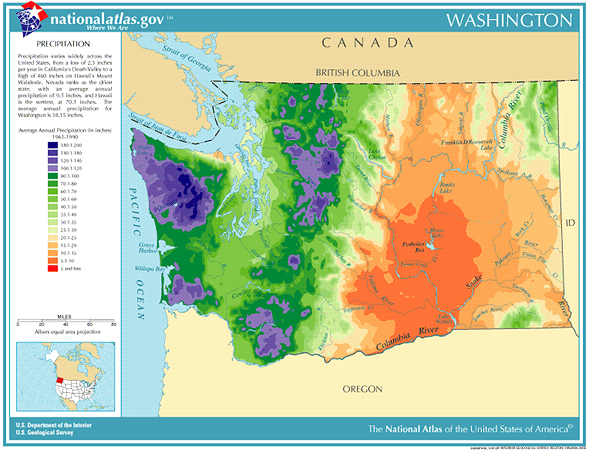
Washington’s precipitation patterns are heavily influenced by its unique geography. The Cascade Mountains, a formidable range running north-south, act as a significant barrier, dictating the state’s rainfall distribution. The western slopes of the Cascades, facing the Pacific Ocean, receive copious amounts of precipitation, often exceeding 100 inches annually. This region is characterized by a temperate rainforest climate, with lush forests and abundant greenery.
In contrast, the eastern slopes of the Cascades, situated in the rain shadow, experience significantly less precipitation. This region, often referred to as the "dry side," receives an average of 10-20 inches of precipitation annually. The arid climate here supports a diverse ecosystem, ranging from grasslands and shrub-steppe to high-elevation alpine meadows.
Seasonal Dance: Understanding Washington’s Precipitation Cycles
Washington’s precipitation patterns are not static but exhibit distinct seasonal variations. The state experiences its wettest months during the fall and winter, coinciding with the arrival of the Pacific storm track. These storms, originating from the Pacific Ocean, bring heavy rain and snowfall to the western slopes of the Cascades.
Spring and summer months generally see a decrease in precipitation, with drier conditions prevailing across most of the state. However, the mountainous regions continue to receive significant snowfall during these months, contributing to the state’s snowpack, a crucial water source for rivers and streams.
Factors Shaping Washington’s Rainfall Landscape
Several factors contribute to the complex precipitation patterns observed in Washington:
- Orographic Lift: The Cascade Mountains play a pivotal role in shaping the state’s precipitation patterns. As moist air from the Pacific Ocean encounters the mountains, it is forced to rise, cooling and condensing into precipitation. This process, known as orographic lift, is responsible for the significant rainfall on the western slopes.
- Pacific Storm Track: The Pacific storm track, a belt of low-pressure systems that travel across the Pacific Ocean, is a primary source of precipitation for Washington. These storms bring rain and snowfall to the state, particularly during the fall and winter months.
- Ocean Currents: The warm currents of the Pacific Ocean, particularly the North Pacific Current, play a role in influencing the amount of moisture available for precipitation. These currents transport warm, moist air towards the coast, contributing to the heavy rainfall in western Washington.
- El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO): This climate pattern, characterized by variations in sea surface temperatures in the central Pacific Ocean, can significantly impact Washington’s precipitation. El Niño events are associated with increased precipitation in the state, particularly during the winter months. Conversely, La Niña events often lead to drier conditions.
The Importance of Precipitation Data: A Multifaceted Role
Understanding Washington’s precipitation patterns is crucial for various sectors, including:
- Agriculture: Farmers rely heavily on precipitation for crop production. Accurate precipitation data helps farmers make informed decisions regarding irrigation, planting schedules, and crop selection.
- Water Management: Precipitation data is essential for managing water resources, including reservoirs, rivers, and groundwater. By understanding precipitation patterns, water managers can anticipate water supply and demand, ensuring efficient allocation and conservation.
- Hydrology: Precipitation data plays a vital role in hydrological modeling, which helps predict river flows, flood risks, and water availability. This information is crucial for flood mitigation, water resource management, and hydropower generation.
- Tourism: Precipitation patterns influence outdoor recreation activities, such as hiking, camping, and skiing. Tourists rely on precipitation data to plan their trips and choose appropriate activities based on weather conditions.
- Environmental Monitoring: Precipitation data provides valuable insights into the state’s environmental health. Monitoring precipitation patterns can help identify trends in air quality, water quality, and ecosystem health.
Washington Precipitation Map: A Visual Tool for Understanding Rainfall Patterns
The Washington precipitation map is a powerful tool for visualizing rainfall patterns across the state. It provides a clear and concise representation of precipitation distribution, allowing users to quickly identify areas receiving high or low rainfall. These maps are typically generated based on historical data, providing a valuable reference for understanding long-term precipitation trends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Washington Precipitation Maps
Q: What is the average annual precipitation in Washington state?
A: The average annual precipitation in Washington state varies significantly depending on location. The western slopes of the Cascades receive an average of 100 inches or more, while the eastern slopes receive an average of 10-20 inches.
Q: What is the wettest month in Washington state?
A: The wettest month in Washington state is typically November, with the highest rainfall occurring on the western slopes of the Cascades.
Q: What is the driest month in Washington state?
A: The driest month in Washington state is typically July, with the lowest rainfall occurring in the eastern part of the state.
Q: How do I access Washington precipitation maps?
A: Washington precipitation maps are available from various sources, including:
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA): NOAA provides a variety of precipitation maps, including historical data and real-time observations.
- Washington State Department of Ecology (Ecology): Ecology provides precipitation data and maps specific to Washington state.
- University of Washington Climate Impacts Group: The Climate Impacts Group provides research and data on climate change impacts in Washington state, including precipitation patterns.
Tips for Using Washington Precipitation Maps
- Understand the map’s scale: Pay attention to the map’s scale and units of measurement to accurately interpret precipitation data.
- Consider the time period: Precipitation maps are often generated based on historical data. Consider the time period covered by the map to understand long-term trends.
- Compare different maps: Compare precipitation maps from different sources to get a comprehensive understanding of rainfall patterns.
- Use maps for planning: Utilize precipitation maps to plan outdoor activities, water management strategies, and agricultural practices.
Conclusion
Washington’s precipitation patterns are a complex and fascinating aspect of the state’s natural environment. Understanding these patterns is crucial for various sectors, including agriculture, water management, tourism, and environmental monitoring. The Washington precipitation map serves as a valuable tool for visualizing rainfall distribution and gaining insights into the state’s unique precipitation landscape. By utilizing this tool and understanding the factors influencing precipitation, we can better manage resources, mitigate risks, and appreciate the diverse ecosystems that thrive in this remarkable state.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Secrets of Washington’s Precipitation: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Rainfall Patterns. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!