Unlocking the Secrets of Ancient Greece: A Geographical Journey
Related Articles: Unlocking the Secrets of Ancient Greece: A Geographical Journey
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Secrets of Ancient Greece: A Geographical Journey. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unlocking the Secrets of Ancient Greece: A Geographical Journey
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unlocking the Secrets of Ancient Greece: A Geographical Journey
- 3.1 The Aegean Sea: A Crossroads of Civilization
- 3.2 The Balkan Peninsula: A Cradle of City-States
- 3.3 Asia Minor: A Bridge to the East
- 3.4 The Importance of Geography in Ancient Greek History
- 3.5 Exploring the Ancient Greek Map: A Journey Through Time
- 3.6 FAQs about the Ancient Greek Map:
- 3.7 Tips for Understanding the Ancient Greek Map:
- 3.8 Conclusion:
- 4 Closure
Unlocking the Secrets of Ancient Greece: A Geographical Journey

The ancient Greek world, a cradle of Western civilization, was not confined to the modern nation-state of Greece. Its influence extended across a vast and diverse geographical tapestry, encompassing the Aegean Sea, the Balkan Peninsula, and parts of Asia Minor. Understanding this geographical context is crucial to comprehending the cultural, political, and economic dynamics that shaped ancient Greek history. This article delves into the intricate map of ancient Greece, exploring its key features, their significance, and the enduring legacy they hold.
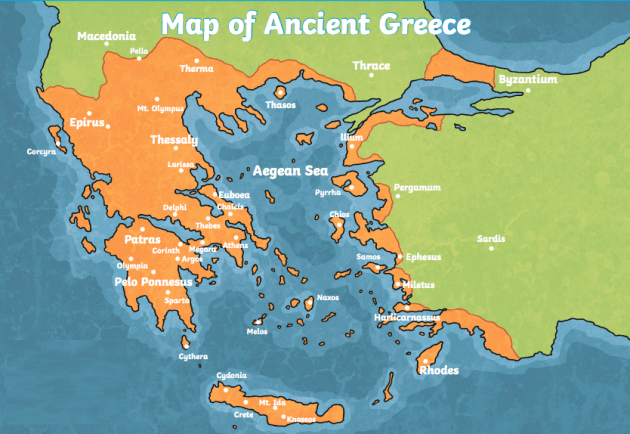
The Aegean Sea: A Crossroads of Civilization
The Aegean Sea, a glittering expanse of blue, played a pivotal role in the development of ancient Greece. Its numerous islands, dotted across its surface like jewels, served as stepping stones for trade and cultural exchange. The sea’s strategic position, connecting the eastern Mediterranean to the Black Sea, made it a vital conduit for maritime trade, facilitating the movement of goods, ideas, and people.
The Aegean Sea’s influence is evident in the myths and legends that permeate Greek literature. Odysseus’s perilous journey, recounted in Homer’s Odyssey, reflects the dangers and allure of the sea. The sea was also the stage for the rise and fall of powerful maritime empires, from the Minoans of Crete to the Athenian naval dominance in the 5th century BC.
The Balkan Peninsula: A Cradle of City-States
The Balkan Peninsula, a rugged and mountainous region, was the heartland of ancient Greece. This landmass, punctuated by fertile valleys and coastal plains, was home to numerous city-states, each with its own distinct identity and governance. The terrain, while challenging, also offered strategic advantages, providing natural barriers and resources.
The mountainous terrain fostered a sense of independence among the city-states, contributing to their rivalry and competition. However, it also facilitated the development of distinct regional cultures, each with its own unique traditions, dialects, and religious beliefs. The Balkan Peninsula was a mosaic of diverse communities, each contributing to the rich tapestry of ancient Greek culture.
Asia Minor: A Bridge to the East
The western coast of Asia Minor, known as Anatolia, was another crucial region for ancient Greece. This region, with its fertile plains and strategic harbors, served as a bridge between Greece and the East, facilitating trade and cultural exchange with the Persian Empire and other civilizations.
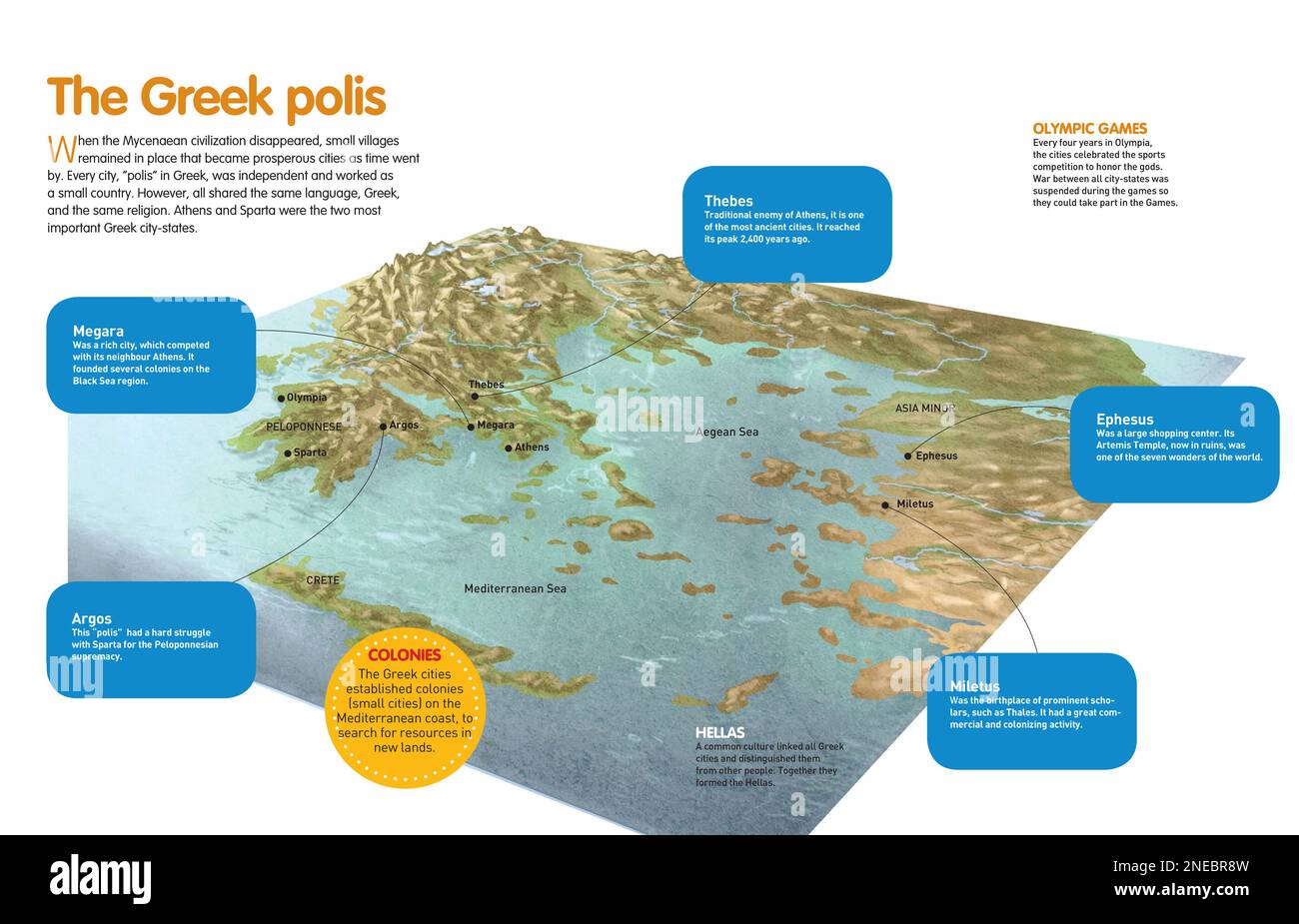
Greek settlements in Asia Minor, known as "colonies," played a vital role in the economic and cultural development of the region. Cities like Ephesus, Miletus, and Smyrna became centers of commerce, art, and learning, contributing significantly to the intellectual and artistic achievements of ancient Greece.
The Importance of Geography in Ancient Greek History
The geographical landscape of ancient Greece profoundly shaped its history, influencing its political structures, economic activities, and cultural development. The sea, the mountains, and the fertile plains provided both challenges and opportunities, shaping the character of the people and their interactions with the world.
Political Structures: The mountainous terrain of the Balkan Peninsula contributed to the rise of independent city-states, each with its own form of government. The rivalry between these city-states, fueled by competition for resources and power, shaped the political landscape of ancient Greece.
Economic Activities: The Aegean Sea and its numerous islands facilitated maritime trade, allowing ancient Greeks to access resources and markets across the Mediterranean. The fertile plains of the Balkan Peninsula and Asia Minor provided agricultural resources, sustaining a growing population.
Cultural Development: The interaction between different cultures through trade and migration enriched the cultural tapestry of ancient Greece. The influence of Eastern civilizations, particularly the Persian Empire, is evident in art, architecture, and philosophy.
Exploring the Ancient Greek Map: A Journey Through Time
To truly understand the significance of ancient Greece’s geography, it is essential to delve into the details of its various regions and cities. This requires a closer examination of the ancient Greek map, analyzing its key features and their impact on history.
Key Features of the Ancient Greek Map:
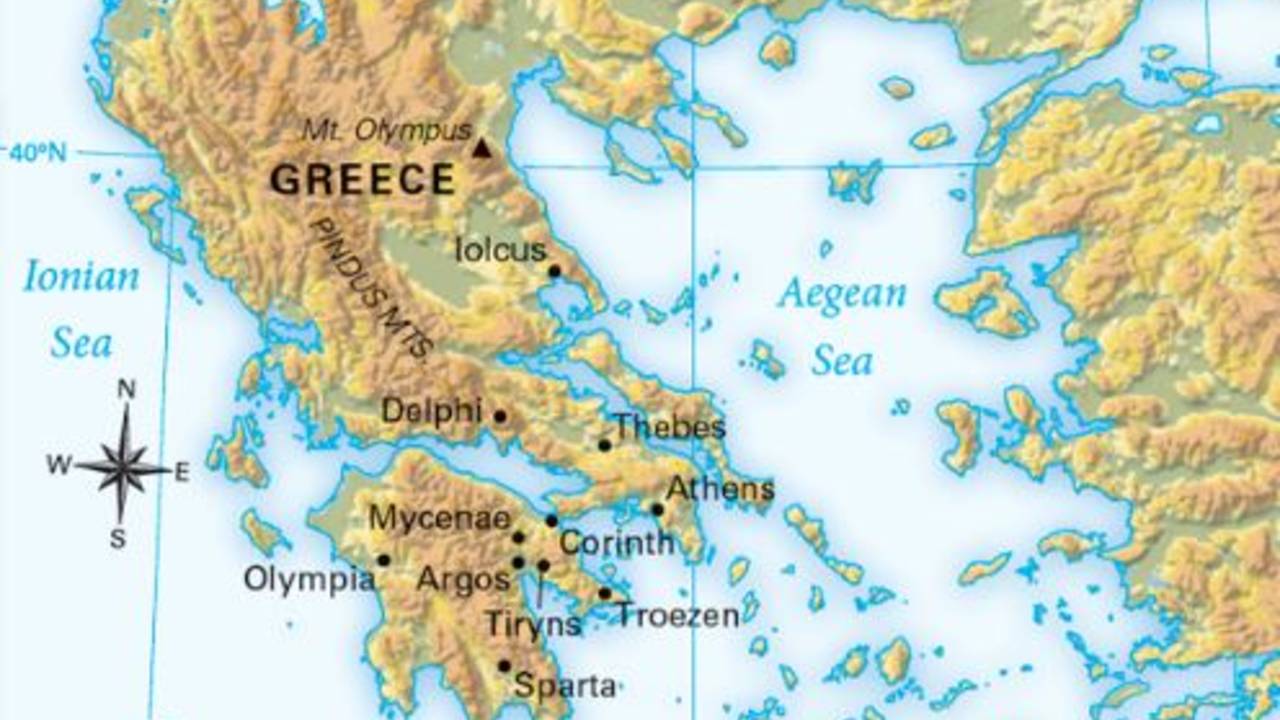
- The Peloponnese: A large peninsula in southern Greece, home to powerful city-states like Sparta and Athens. Its mountainous terrain and fertile valleys played a significant role in the development of Spartan military prowess and Athenian democracy.
- Central Greece: This region, encompassing the city of Thebes, was strategically located between the Peloponnese and northern Greece, making it a crucial battleground during the Peloponnesian War.
- Northern Greece: This region, with its fertile plains and strategic location, was home to powerful kingdoms like Macedon, which ultimately unified Greece under Alexander the Great.
- The Aegean Islands: These islands, scattered across the Aegean Sea, played a vital role in trade and cultural exchange. They were also centers of religious and artistic development, with unique traditions and beliefs.
- Asia Minor: The western coast of Asia Minor was home to numerous Greek colonies, which played a significant role in the economic and cultural development of the region.
Key Cities and Their Significance:
- Athens: The birthplace of democracy, philosophy, and art, Athens was a major center of intellectual and cultural activity. Its strategic location on the Aegean Sea facilitated trade and cultural exchange.
- Sparta: Known for its military prowess and strict social system, Sparta was a powerful city-state that dominated the Peloponnese. Its military strength and political influence played a significant role in the history of ancient Greece.
- Thebes: Located in central Greece, Thebes was a strategically important city-state that played a crucial role in the Peloponnesian War.
- Delphi: A sacred site dedicated to the god Apollo, Delphi was a major religious center, attracting pilgrims from across the ancient Greek world.
- Olympia: The site of the ancient Olympic Games, Olympia was a sacred sanctuary dedicated to the god Zeus. The games, held every four years, were a significant cultural and religious event, bringing together athletes and spectators from across the Greek world.
FAQs about the Ancient Greek Map:
Q1: What was the most important geographical feature of ancient Greece?
A: The Aegean Sea was arguably the most important geographical feature of ancient Greece, facilitating trade, cultural exchange, and the rise of powerful maritime empires.
Q2: What were the main differences between the city-states of Athens and Sparta?
A: Athens was known for its democracy, intellectual prowess, and cultural achievements, while Sparta was a militaristic society with a strict social system.
Q3: How did the geography of ancient Greece influence its political structure?
A: The mountainous terrain of the Balkan Peninsula contributed to the rise of independent city-states, each with its own form of government. The rivalry between these city-states, fueled by competition for resources and power, shaped the political landscape of ancient Greece.
Q4: What was the impact of Greek colonies in Asia Minor?
A: Greek colonies in Asia Minor played a significant role in the economic and cultural development of the region, contributing to the spread of Greek culture and ideas.
Q5: How did the ancient Greek map change over time?
A: The ancient Greek map evolved over time, with the expansion of Greek settlements, the rise and fall of empires, and the changing political landscape.
Tips for Understanding the Ancient Greek Map:
- Use a reliable map: Refer to a detailed and accurate map of ancient Greece to visualize the geographical features, cities, and regions.
- Study the major regions: Familiarize yourself with the key regions of ancient Greece, including the Peloponnese, Central Greece, Northern Greece, the Aegean Islands, and Asia Minor.
- Learn about the key cities: Understand the significance of major cities like Athens, Sparta, Thebes, Delphi, and Olympia, and their role in ancient Greek history.
- Connect geography to history: Recognize how geographical features influenced political structures, economic activities, and cultural development.
- Explore primary sources: Examine ancient texts, inscriptions, and archaeological evidence to gain a deeper understanding of the geography of ancient Greece.
Conclusion:
The ancient Greek map is a testament to the enduring legacy of this civilization. It provides a window into the past, revealing the intricate relationships between geography, culture, and history. By exploring this map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and richness of the ancient Greek world, its enduring influence on Western civilization, and the timeless lessons it holds for us today.




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/History_of_Greece_for_High_Schools_and_Academies_1899_14576880059-9b79528371d3443089862b67a1fbc002.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Secrets of Ancient Greece: A Geographical Journey. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!