The Shifting Sands Of War: A Geographic Analysis Of Germany In World War II
The Shifting Sands of War: A Geographic Analysis of Germany in World War II
Related Articles: The Shifting Sands of War: A Geographic Analysis of Germany in World War II
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Shifting Sands of War: A Geographic Analysis of Germany in World War II. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Shifting Sands of War: A Geographic Analysis of Germany in World War II
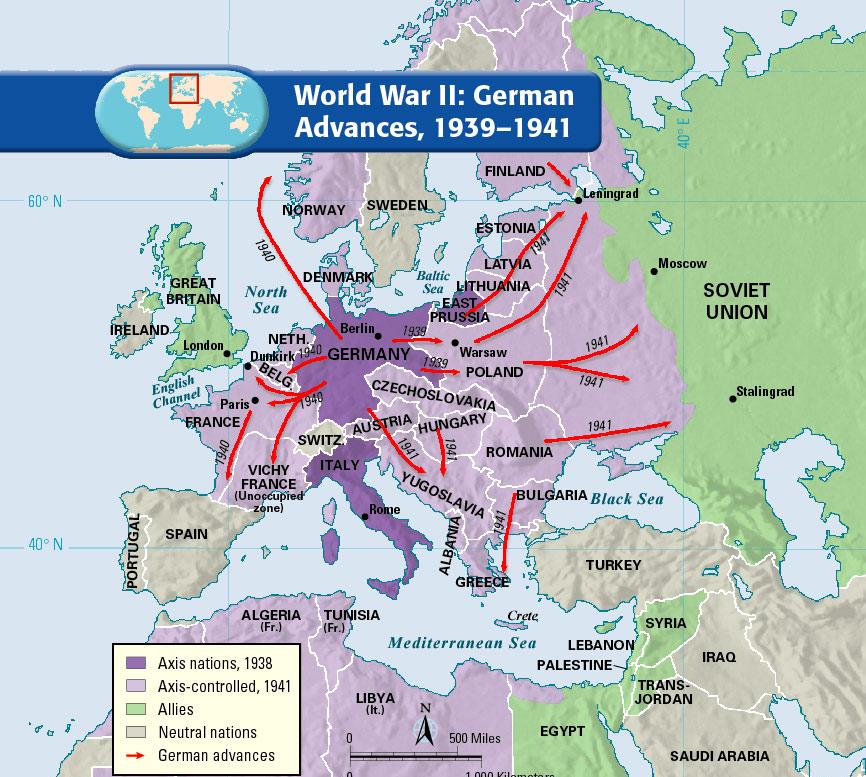
The Second World War, a global conflict of unprecedented scale and devastation, saw Germany at the heart of the storm. Understanding the geographic context of Germany’s military operations and territorial ambitions is crucial for comprehending the war’s course and its lasting impact. This analysis delves into the interplay of geography and strategy in Germany’s wartime actions, focusing on the evolving map of Nazi-occupied Europe and the strategic implications of key locations.
Germany’s Geographic Advantages and Challenges
Germany’s location in Central Europe, a natural crossroads of trade routes and cultural exchange, presented both opportunities and challenges. Its central position allowed for swift deployment of troops across multiple fronts, but also exposed it to potential attacks from multiple directions. The country’s diverse landscape, ranging from the North German Plain to the rugged Alps, offered both strategic advantages and logistical obstacles.
The Blitzkrieg and the Early Conquests
Germany’s initial success was largely attributed to its innovative military strategy, the "Blitzkrieg," which relied on rapid, mechanized advances and overwhelming air power. The conquest of Poland in 1939, achieved through a coordinated attack from multiple directions, demonstrated the effectiveness of this strategy. This early success paved the way for the invasion of Denmark and Norway, securing vital access to the North Sea and crucial resources.
The Expansion of the Reich: A Map of Occupation
The map of Europe during World War II underwent a dramatic transformation as Germany’s territorial ambitions expanded. The occupation of France, the Netherlands, Belgium, and Luxembourg in 1940 brought vast swathes of territory under Nazi control. This expansion provided Germany with access to vital resources, including industrial centers and agricultural land, while simultaneously crippling the Allied war effort.
The Eastern Front: A Brutal Struggle
The invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941 marked a turning point in the war, shifting the focus to a vast and brutal conflict on the Eastern Front. The vast distances, harsh weather conditions, and fierce resistance of the Red Army presented immense challenges for the German war machine. Despite initial successes, the Eastern Front ultimately became a quagmire, draining German resources and manpower.
The Importance of Key Locations
- The Ruhr Valley: This heavily industrialized region in western Germany was crucial for supplying the German war machine with steel, coal, and other essential materials.
- The Rhineland: This strategic border region provided a buffer against potential attacks from France and allowed Germany to control the Rhine River, a vital waterway for trade and transportation.
- The Baltic Sea: Control of the Baltic Sea was essential for Germany to secure access to vital resources from Scandinavia and the Soviet Union.
- The North Sea: This important waterway facilitated Germany’s naval operations and provided access to vital ports and shipping lanes.
The Impact of Geographic Factors on Wartime Strategies
The geographic landscape played a significant role in shaping the course of the war. The rugged terrain of the Alps and the Carpathian Mountains provided natural defensive positions for German forces, while the vast plains of Eastern Europe facilitated large-scale tank battles. The strategic importance of key waterways, such as the Rhine, the Danube, and the Baltic Sea, influenced the deployment of naval forces and the flow of supplies.
The Legacy of the War: A Shifting Map of Europe
The end of World War II saw a redrawing of the European map, with Germany losing significant territory and facing a period of division. The war’s devastation and the subsequent Cold War left a lasting impact on the political and economic landscape of Europe, shaping its future for decades to come.
FAQs about Germany’s Map in World War II
Q: How did Germany’s geographic location influence its military strategy?
A: Germany’s central location in Europe allowed for rapid troop deployment across multiple fronts. The diverse landscape presented both strategic advantages and logistical challenges.
Q: What were the key geographic factors that contributed to Germany’s initial successes?
A: The "Blitzkrieg" strategy, the conquest of Poland, and the securement of vital resources from occupied territories were all influenced by geographic factors.
Q: Why was the Eastern Front so crucial in the war?
A: The Eastern Front was a vast and brutal conflict that drained German resources and manpower. The geographic challenges of the region, including harsh weather and vast distances, played a significant role in the war’s outcome.
Q: What were the long-term consequences of Germany’s territorial expansion?
A: The war’s devastation and the subsequent division of Germany left a lasting impact on the political and economic landscape of Europe.
Tips for Studying the Geographic Impact of World War II
- Utilize maps: Studying historical maps of Europe during World War II can provide valuable insights into the geographic context of the war.
- Analyze key battles: Examining the geographic factors that influenced major battles can help understand the strategic importance of specific locations.
- Research the impact of resources: Understanding the role of resources, such as oil, coal, and food, in the war effort can reveal the strategic importance of certain territories.
- Explore the impact on civilian populations: Studying the impact of the war on civilian populations can provide a more nuanced understanding of the human cost of conflict.
Conclusion
The map of Germany in World War II is a testament to the complex interplay of geography and strategy. By understanding the geographic context of the war, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the challenges faced by both sides and the lasting impact of the conflict on the world. The war’s legacy serves as a reminder of the importance of understanding the strategic implications of geographic factors in shaping the course of history.

![[Map] Map depicting the Allied campaign toward Germany, 26 Aug-14 Sep](http://ww2db.com/images/battle_liberationofbelgium6.jpg)





![[Map] Map depicting the final campaign in Germany, 19 Apr-7 May 1945](http://ww2db.com/images/battle_berlin11.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Shifting Sands of War: A Geographic Analysis of Germany in World War II. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!