The Muslim World: Mapping a Diverse and Dynamic Landscape
Related Articles: The Muslim World: Mapping a Diverse and Dynamic Landscape
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Muslim World: Mapping a Diverse and Dynamic Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Muslim World: Mapping a Diverse and Dynamic Landscape
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Muslim World: Mapping a Diverse and Dynamic Landscape
- 3.1 Understanding the Muslim Map: Beyond Demographics
- 3.2 The Importance of the Muslim Map: A Framework for Understanding
- 3.3 Beyond the Map: Engaging with the Muslim World
- 3.4 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
- 3.5 Tips for Engaging with the Muslim World:
- 3.6 Conclusion: A Path Towards Understanding
- 4 Closure
The Muslim World: Mapping a Diverse and Dynamic Landscape

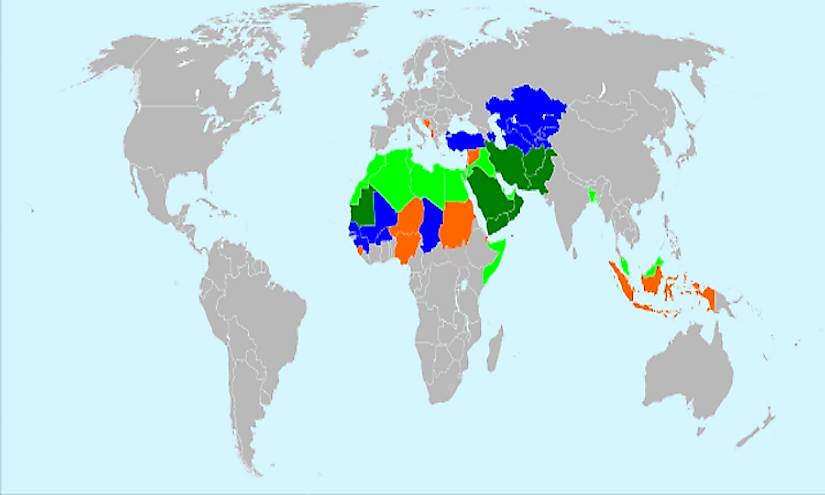
The term "Muslim map" is often used to describe a visual representation of the global distribution of Muslims. However, this understanding is reductive and overlooks the intricate tapestry of cultural, religious, and historical nuances that define the Muslim world. A more accurate approach is to view the Muslim map as a dynamic representation of a diverse and interconnected community, spanning continents and encompassing a vast spectrum of beliefs, practices, and experiences.
Understanding the Muslim Map: Beyond Demographics
The Muslim map is not merely a geographical representation of Muslim populations. It reflects a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Historical Influences: The spread of Islam, originating in the Arabian Peninsula, has been shaped by centuries of migration, trade, conquest, and cultural exchange. This historical journey is reflected in the geographical distribution of Muslim communities, their distinct cultural identities, and their diverse interpretations of Islamic teachings.
- Religious Diversity: The Muslim world is not monolithic. It encompasses a range of denominations, sects, and schools of thought, each with its own interpretations of Islamic doctrines and practices. This diversity is reflected in the Muslim map, showcasing the vibrant mosaic of Islamic thought and practice.
- Cultural Expressions: The Muslim map embodies the richness and diversity of Muslim cultures. From the vibrant art and architecture of the Middle East to the Sufi music and dance traditions of South Asia, the map reflects the unique cultural expressions that have evolved within different Muslim communities.
- Political Landscape: The Muslim world is characterized by a diverse political landscape, encompassing nation-states, autonomous regions, and areas with complex geopolitical dynamics. The Muslim map provides a framework for understanding the political realities of Muslim communities and their interactions with the wider world.
The Importance of the Muslim Map: A Framework for Understanding
The Muslim map serves as a crucial tool for understanding the Muslim world, offering valuable insights into:
- Global Distribution: The map helps visualize the geographical spread of Muslim populations, highlighting their presence in various continents and regions. This provides a foundation for understanding the demographics and global reach of the Muslim community.
- Cultural Diversity: The map underscores the rich tapestry of cultures that exist within the Muslim world. It showcases the unique traditions, languages, and artistic expressions that have emerged within different Muslim communities.
- Religious Landscape: The map helps navigate the diverse religious landscape of the Muslim world, highlighting the presence of different denominations, sects, and schools of thought. This understanding is essential for fostering interfaith dialogue and promoting religious tolerance.
- Political Dynamics: The map provides a framework for understanding the political realities of the Muslim world, including the challenges and opportunities faced by Muslim communities in different contexts. This knowledge is crucial for engaging in constructive dialogue and addressing global issues related to the Muslim world.
Beyond the Map: Engaging with the Muslim World
While the Muslim map provides a valuable visual representation, it is essential to move beyond the static image and engage with the Muslim world through:
- Direct Engagement: Building relationships with Muslim communities through dialogue, cultural exchange, and collaborative initiatives is crucial for fostering understanding and respect.
- Research and Scholarship: Engaging with academic research and scholarly work on Islam and the Muslim world provides deeper insights into the complexities and nuances of this diverse community.
- Media Literacy: Developing critical media literacy skills helps discern accurate and nuanced information about the Muslim world, avoiding generalizations and stereotypes.
- Interfaith Dialogue: Engaging in constructive interfaith dialogue fosters understanding, breaks down barriers, and promotes peaceful coexistence.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
1. What is the total population of Muslims worldwide?
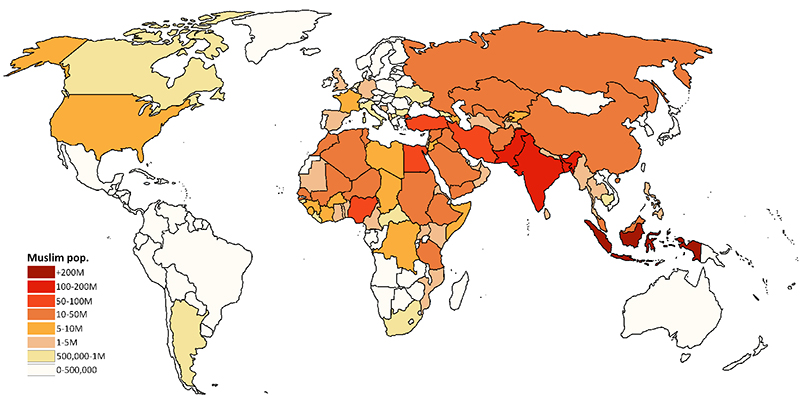
According to the Pew Research Center, there were approximately 1.9 billion Muslims worldwide in 2020. This makes Islam the second-largest religion in the world, after Christianity.
2. Which countries have the largest Muslim populations?
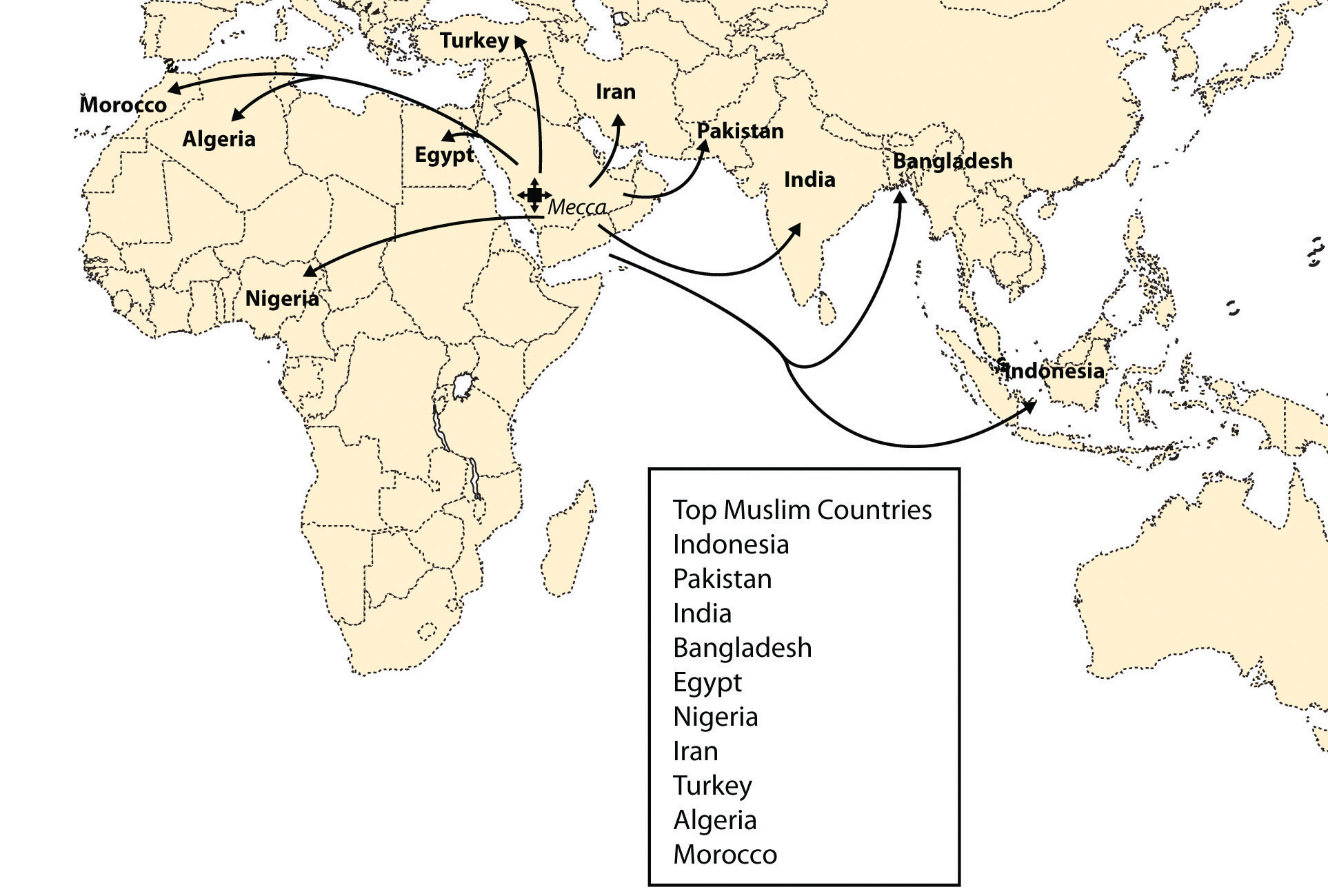
The countries with the largest Muslim populations are Indonesia, Pakistan, India, Bangladesh, and Nigeria. These countries are home to a significant proportion of the global Muslim population.
3. What are the main denominations of Islam?
The two main denominations of Islam are Sunni and Shia. While they share core beliefs, they differ in their interpretations of certain aspects of Islamic doctrine and practice.
4. How does the Muslim map reflect the history of Islam?
The Muslim map reflects the historical spread of Islam through migration, trade, conquest, and cultural exchange. The geographical distribution of Muslim communities, their distinct cultural identities, and their diverse interpretations of Islamic teachings are all shaped by their historical experiences.
5. What are some challenges faced by Muslim communities today?
Muslim communities face various challenges, including discrimination, Islamophobia, political instability, and economic disparities. These challenges require collaborative efforts to address and promote inclusivity and social justice.
Tips for Engaging with the Muslim World:
- Respect Cultural Differences: Recognize and respect the diversity of cultural expressions within the Muslim world, avoiding generalizations and stereotypes.
- Learn about Islam: Engage with resources and materials that provide accurate information about Islamic beliefs, practices, and history.
- Embrace Dialogue: Seek opportunities for constructive dialogue with Muslim individuals and communities, fostering understanding and building bridges.
- Challenge Islamophobia: Speak out against Islamophobia and promote tolerance and respect for all faiths.
- Support Muslim Initiatives: Engage with and support organizations and initiatives that promote peace, social justice, and understanding within the Muslim world.
Conclusion: A Path Towards Understanding
The Muslim map serves as a valuable starting point for understanding the diverse and dynamic landscape of the Muslim world. However, it is crucial to move beyond the static image and engage with the Muslim community through dialogue, research, and collaborative efforts. By embracing diversity, fostering understanding, and promoting respect, we can contribute to a more inclusive and harmonious world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Muslim World: Mapping a Diverse and Dynamic Landscape. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!