Navigating The Shifting Sands Of War: A Comprehensive Look At The Map Of Germany In World War II
Navigating the Shifting Sands of War: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Germany in World War II
Related Articles: Navigating the Shifting Sands of War: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Germany in World War II
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Shifting Sands of War: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Germany in World War II. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Shifting Sands of War: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Germany in World War II

The map of Germany during World War II is not simply a static representation of borders. It is a dynamic tapestry woven with the threads of conquest, resistance, and shifting alliances. Understanding the geographical changes and strategic movements during the conflict is crucial for grasping the complexities of this defining historical period.
The Shifting Landscape of War:
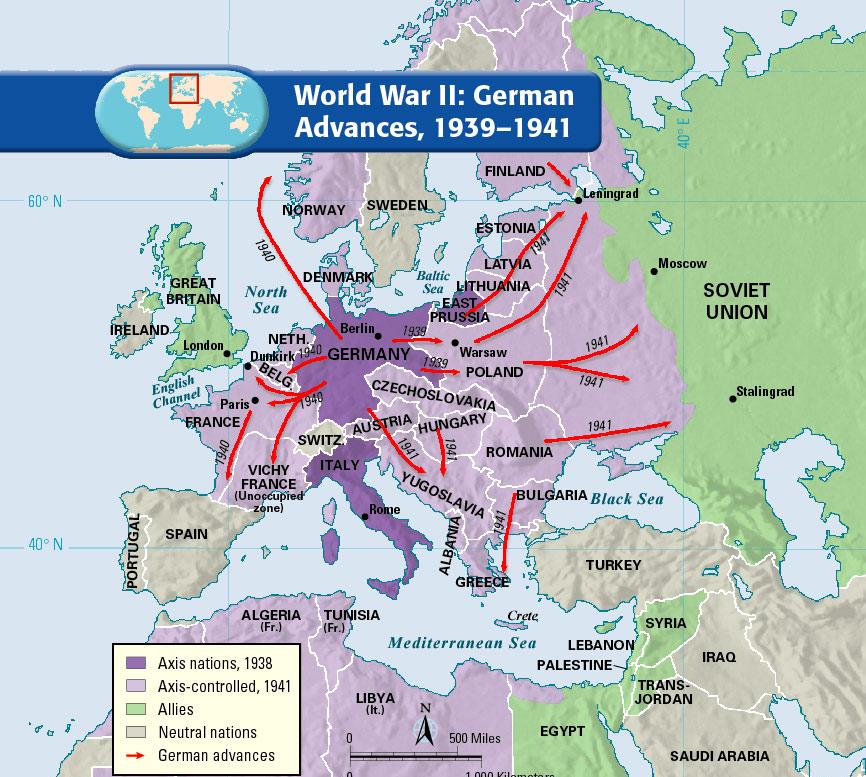
At the war’s outset in 1939, Germany’s borders were relatively compact, encompassing the territory of the Weimar Republic. However, the Nazi regime’s aggressive expansionist policy rapidly altered this landscape.
- The Blitzkrieg and the Rise of the Third Reich: The initial years of the war saw Germany’s lightning-fast military campaigns, known as the Blitzkrieg, conquer vast swathes of Europe. Poland, Denmark, Norway, the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and France fell under Nazi control. This expansion dramatically increased the geographical footprint of the Third Reich.
- The Eastern Front: A Brutal Struggle: The invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941 marked a turning point in the war. The Eastern Front became a brutal theatre of attrition, characterized by immense casualties and devastating destruction. Germany’s control over vast stretches of Eastern Europe, including Ukraine, Belarus, and the Baltic states, fueled its war machine but also stretched its resources thin.
- The Allied Counteroffensive and the Shrinking Reich: As the war progressed, the tide began to turn against Germany. Allied forces, particularly the Soviet Union and the United States, pushed back, liberating occupied territories and gradually shrinking the Nazi-controlled areas.
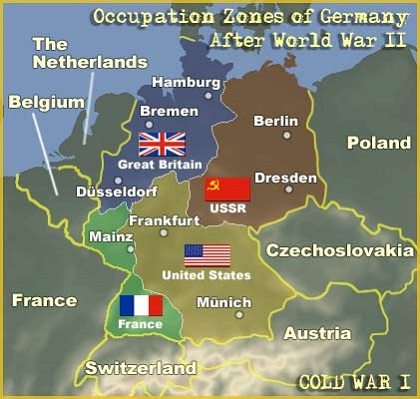
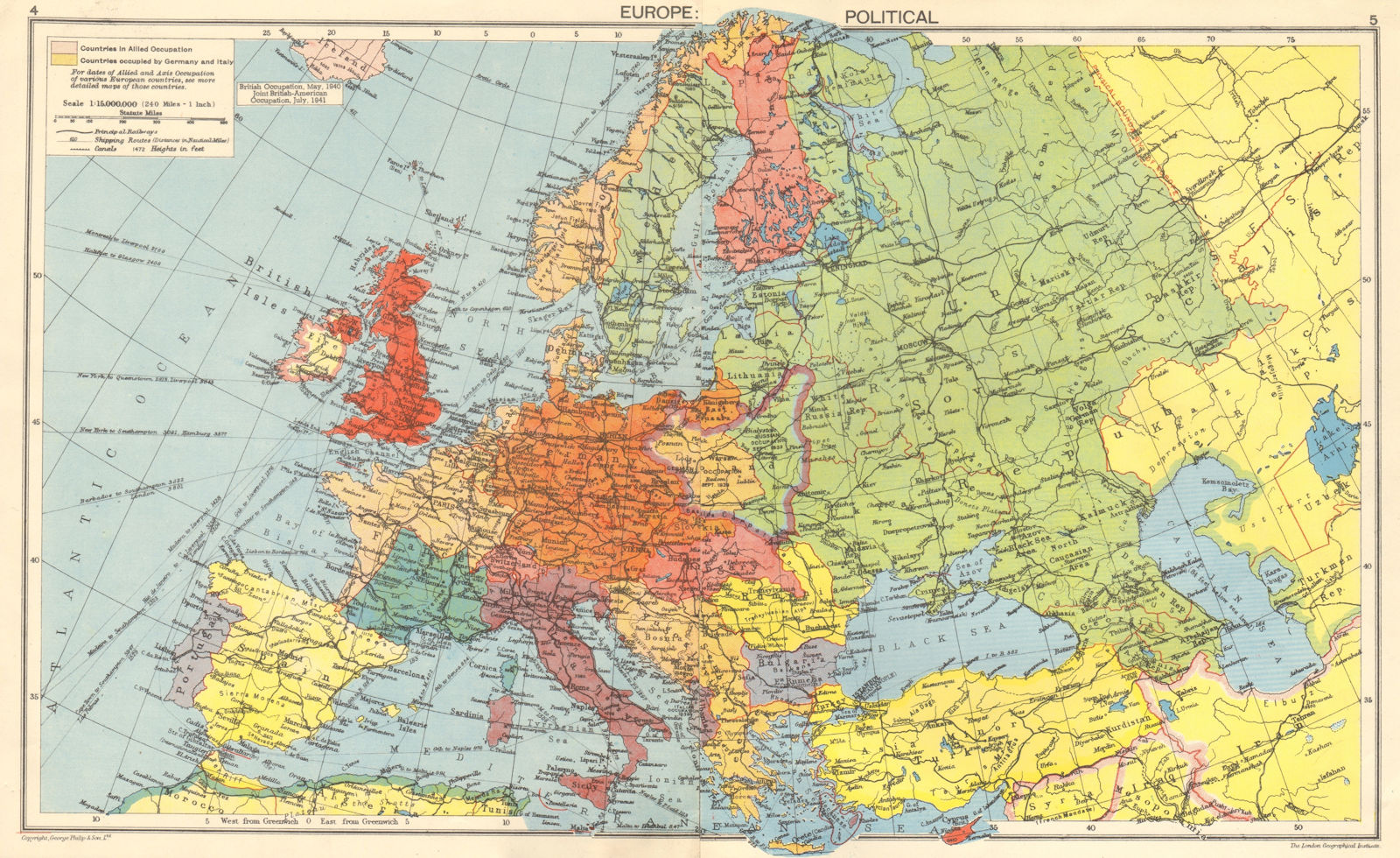
- The Final Collapse and the Division of Germany: By 1945, Germany was on the brink of collapse. The country was divided into four occupation zones, controlled by the Allied powers: the United States, the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union, and France. This division laid the foundation for the Cold War and the eventual emergence of East and West Germany.
The Importance of the Map:
The map of Germany during World War II offers a vital tool for understanding the war’s complexities. It provides a visual representation of:
- The scope of German expansion: The map vividly illustrates the extent of Nazi Germany’s territorial ambitions and the vast areas it controlled during the war.
- Strategic considerations: It helps analyze the strategic choices made by both sides, including the locations of battlefronts, supply lines, and key strategic points.
- The impact of geography: The map highlights how geographical features, such as mountain ranges, rivers, and coastlines, influenced military operations and logistics.
- The human cost of war: The map reveals the devastation wrought by the war, showing the areas subjected to intense fighting, bombing raids, and occupation.
Beyond the Boundaries: Understanding the Human Element:
While the map provides a crucial framework for understanding the war’s geographical dimensions, it is essential to remember that it is a representation of human experiences. Behind the lines, behind the battles, and within the occupied territories, individuals lived through the war’s horrors and its consequences.
- The Resistance: The map does not depict the countless acts of resistance against Nazi rule, both within Germany and in occupied territories. From the French Resistance to the Polish Underground, individuals risked their lives to challenge the Nazi regime.
- The Holocaust: The map cannot fully convey the unspeakable tragedy of the Holocaust, a systematic campaign of genocide that targeted Jews and other minorities across Europe.
- The Civilian Experience: The map does not capture the daily lives of civilians caught in the war’s crossfire, struggling with food shortages, displacement, and the constant threat of violence.
Engaging with the Map: A Path to Deeper Understanding:
Exploring the map of Germany during World War II offers a unique opportunity to:
- Visualize the complexities of the war: The map serves as a powerful visual aid, allowing for a deeper understanding of the war’s geographical dynamics.
- Gain historical perspective: Studying the map helps contextualize historical events, providing a deeper understanding of the war’s motivations, strategies, and consequences.
- Reflect on the human cost of war: The map serves as a reminder of the devastating impact of war on individuals, communities, and entire nations.
FAQs: Demystifying the Map of Germany in World War II
1. What were the key geographical features that influenced the course of the war?
The geography of Europe played a significant role in shaping the war’s course. Mountain ranges, such as the Alps and the Carpathians, hindered military movements and provided defensive positions. Rivers, including the Rhine and the Danube, served as natural barriers and crucial supply routes. Coastal regions, like the Baltic Sea and the North Sea, were vital for naval operations and submarine warfare.
2. What were the major battlefronts in World War II?
The war saw several major battlefronts:
- The Western Front: This front spanned from the Atlantic Ocean to the Rhine River, witnessing intense fighting between Germany and the Allied forces.
- The Eastern Front: This front extended from the Baltic Sea to the Black Sea, characterized by brutal fighting between Germany and the Soviet Union.
- The Mediterranean Front: This front encompassed Italy, Greece, and North Africa, witnessing battles between Germany and the Allied forces.
- The Pacific Front: This front, primarily fought between Japan and the Allied forces, involved the battles for islands in the Pacific Ocean.
3. How did the map of Germany change throughout the war?
Germany’s territorial control expanded significantly at the war’s outset, encompassing vast areas of Europe. As the war progressed, the Allied forces pushed back, liberating occupied territories and gradually shrinking the Nazi-controlled areas. By the war’s end, Germany had been divided into four occupation zones, controlled by the Allied powers.
4. What are the historical implications of the map of Germany in World War II?
The map of Germany during World War II serves as a powerful reminder of the devastating consequences of war and the importance of peaceful conflict resolution. It also highlights the complex geopolitical dynamics that shaped the world in the 20th century and continue to influence international relations today.
Tips for Understanding the Map:
- Use a comprehensive atlas: A detailed atlas with maps of Europe during World War II will provide a comprehensive overview of the war’s geographical dimensions.
- Focus on specific regions: To gain a deeper understanding of the war’s complexities, focus on specific regions, such as the Eastern Front or the Western Front.
- Explore primary sources: Primary sources, such as diaries, letters, and photographs, can offer personal perspectives on the war’s impact on individuals and communities.
- Engage with historical research: Consult scholarly articles and books to gain insights into the war’s strategic considerations and the role of geography in shaping its course.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Conflict and Transformation
The map of Germany during World War II is a potent symbol of the war’s devastation and the enduring legacy of conflict and transformation. It serves as a reminder of the human cost of war and the importance of preserving peace. Studying the map, with its intricate details and shifting boundaries, offers a unique opportunity to understand the complexities of the war, its lasting impact, and the lessons it holds for the future. By engaging with the map and its historical context, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the past and strive for a more peaceful future.




![What territories did Germany lose after World War 2? [MAP] Germany](https://i.pinimg.com/originals/d8/08/08/d808087a1acc3b6771dcbe40a97b569b.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Shifting Sands of War: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Germany in World War II. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!