Navigating The Landscape Of Knowledge: A Comprehensive Guide To Education Concept Maps
Navigating the Landscape of Knowledge: A Comprehensive Guide to Education Concept Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Knowledge: A Comprehensive Guide to Education Concept Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Knowledge: A Comprehensive Guide to Education Concept Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Knowledge: A Comprehensive Guide to Education Concept Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Landscape of Knowledge: A Comprehensive Guide to Education Concept Maps
- 3.1 Understanding the Essence of Concept Maps
- 3.2 The Benefits of Education Concept Maps: Unlocking the Potential of Knowledge
- 3.3 Applications of Education Concept Maps: A Wide Spectrum of Use Cases
- 3.4 FAQs About Education Concept Maps: Addressing Common Queries
- 3.5 Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Visual Learning
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Landscape of Knowledge: A Comprehensive Guide to Education Concept Maps

In the ever-evolving world of education, where information proliferates at an unprecedented rate, effective learning strategies are paramount. One such strategy, gaining increasing prominence, is the use of concept maps. These visual tools serve as powerful instruments for organizing, understanding, and retaining knowledge.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of education concept maps, exploring their structure, benefits, and applications across diverse learning contexts.
Understanding the Essence of Concept Maps
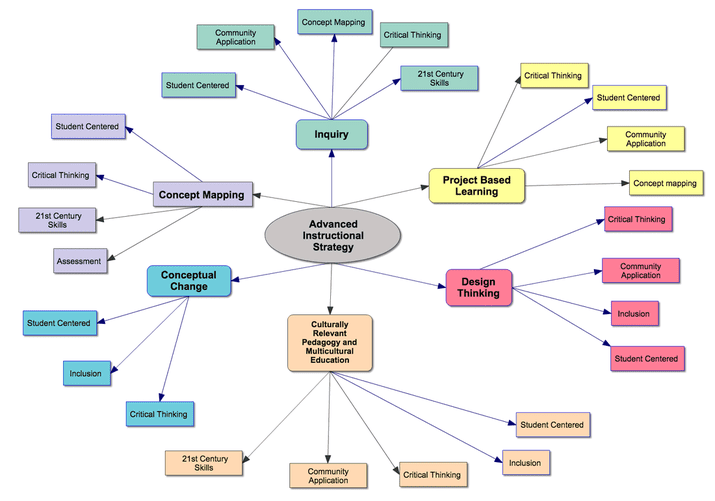
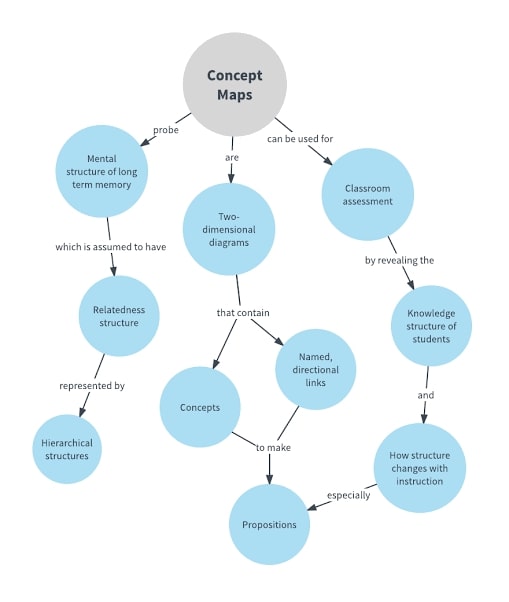
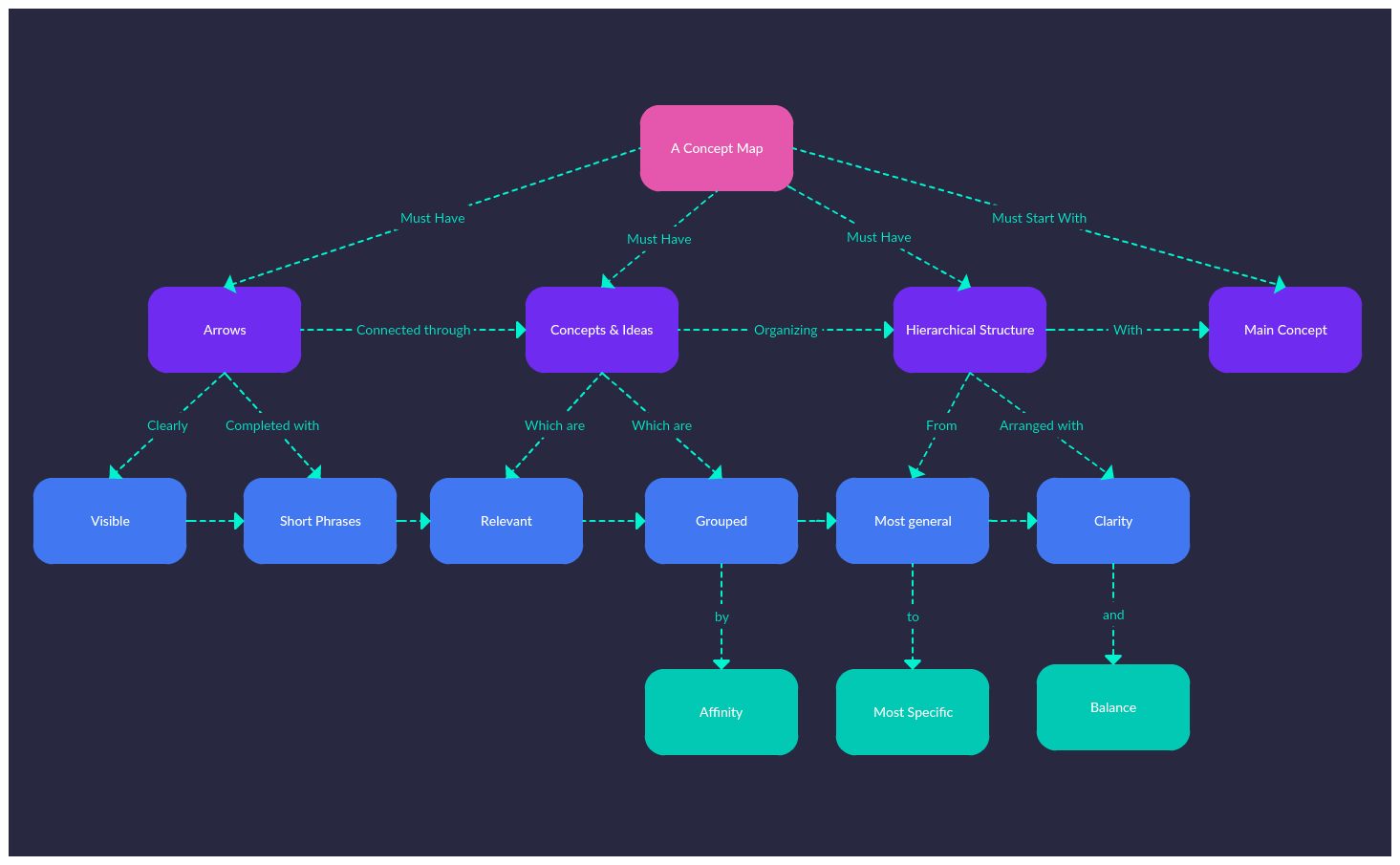
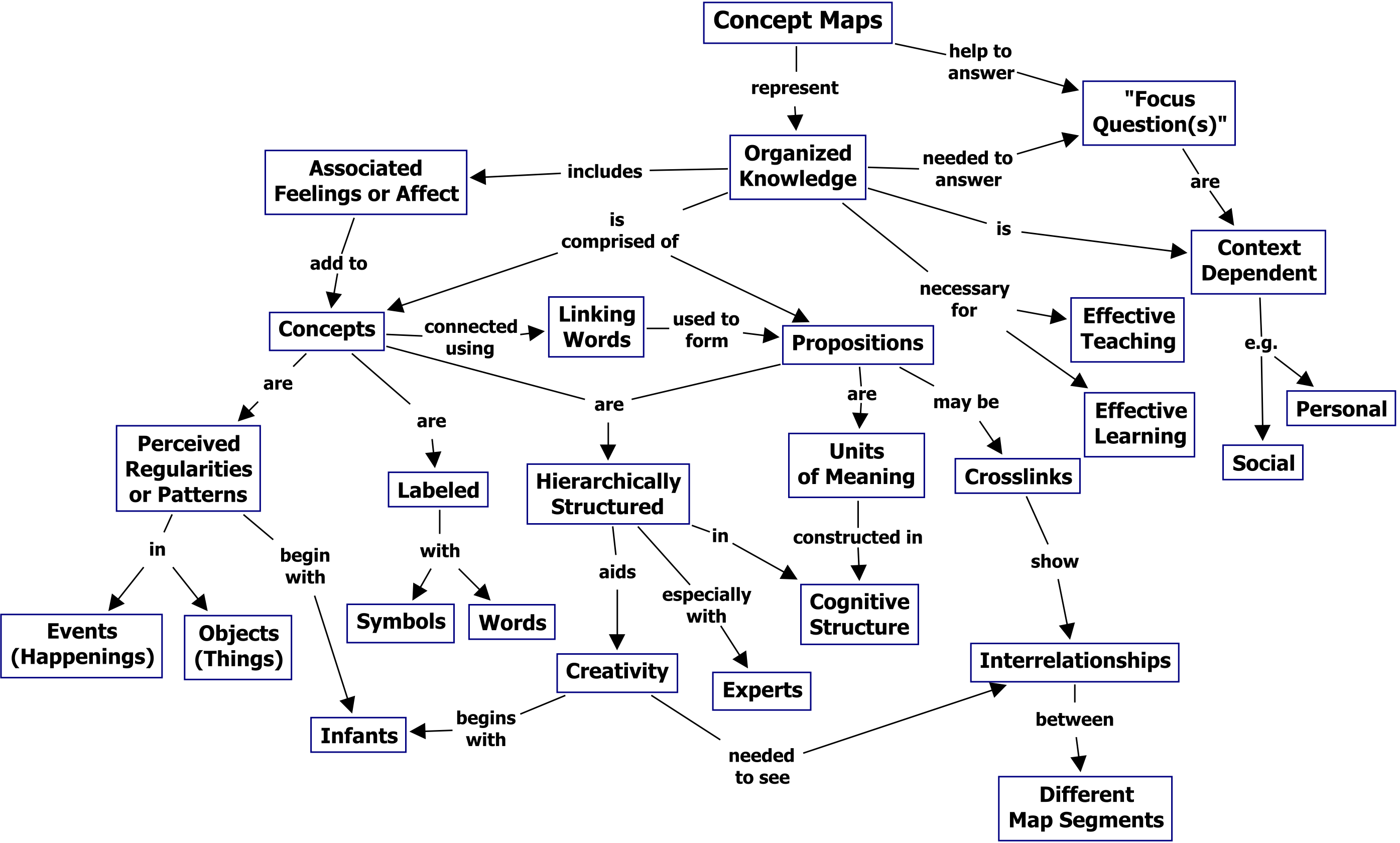
At its core, a concept map is a graphical representation of knowledge, illustrating the relationships between different concepts. It transcends simple listing of facts, instead fostering a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of information.
Key Components of a Concept Map:
- Nodes: These represent the core concepts or ideas within a given topic. They are typically enclosed in boxes or circles, with each node containing a concise, specific term or phrase.
- Links: Lines or arrows connecting the nodes, signifying the relationships between concepts. These links are often accompanied by brief phrases or verbs, clarifying the nature of the connection (e.g., "causes," "leads to," "is a type of").
- Hierarchies: Concept maps often exhibit a hierarchical structure, with more general concepts positioned higher and more specific concepts branching out lower. This visual hierarchy reflects the organization of knowledge from broad to specific.
The Power of Visual Representation:
The visual nature of concept maps offers several advantages:
- Enhanced Comprehension: By presenting information visually, concept maps engage multiple cognitive processes, facilitating deeper understanding and retention.
- Improved Organization: The structured arrangement of concepts promotes logical thinking and helps learners identify the key elements and relationships within a topic.
- Active Learning: Concept mapping encourages active participation in the learning process, as learners engage in identifying, organizing, and connecting concepts.
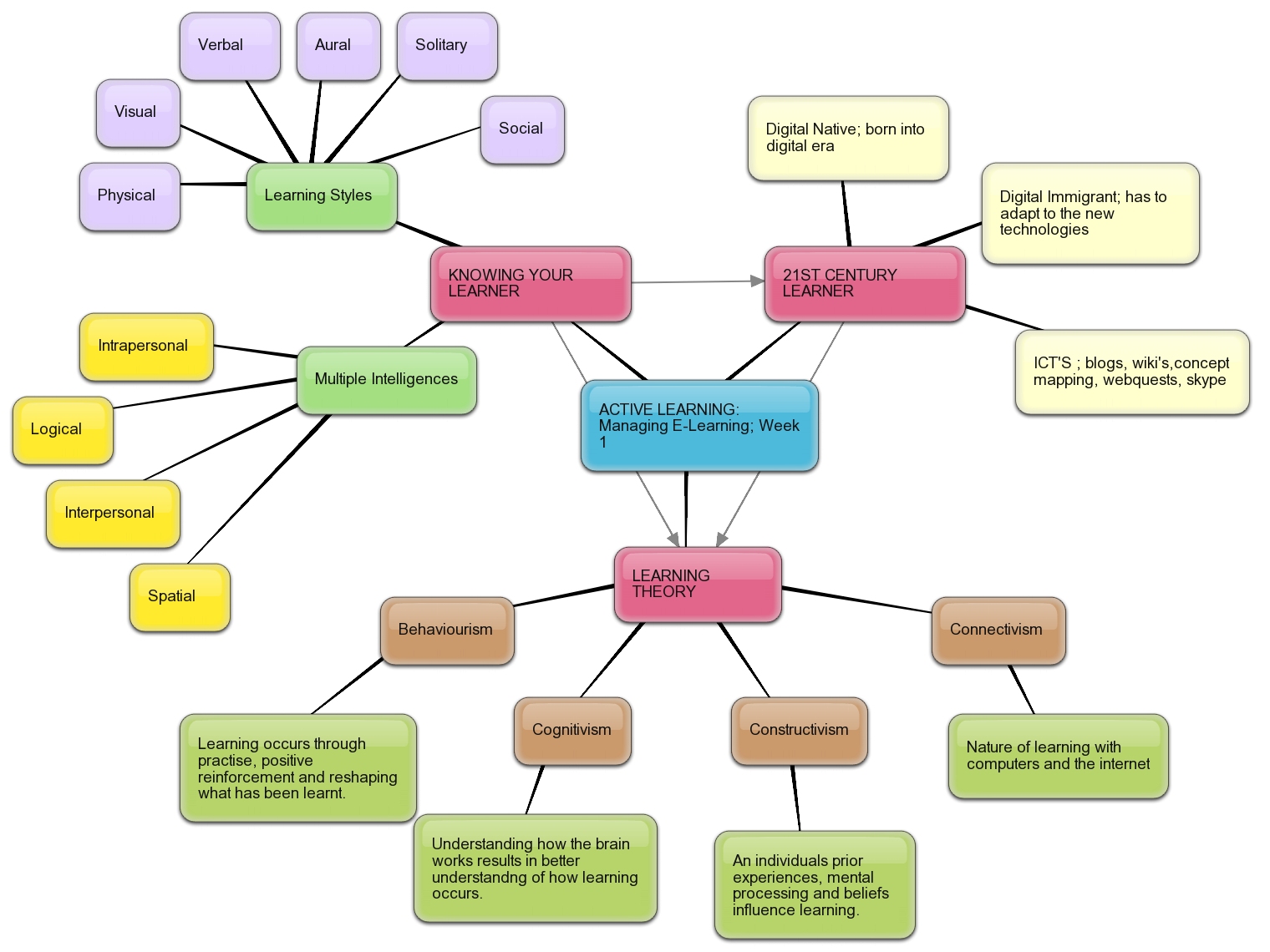
- Individualized Learning: Concept maps can be tailored to individual learning styles and preferences, providing a personalized learning experience.
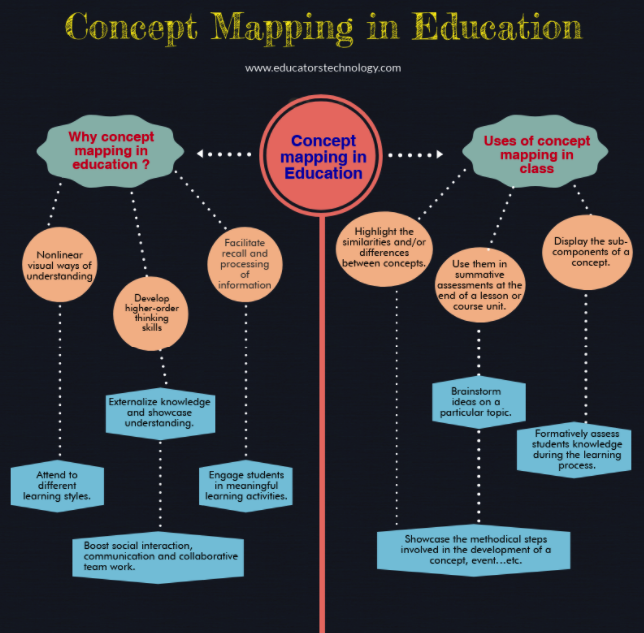
The Benefits of Education Concept Maps: Unlocking the Potential of Knowledge
Concept maps are not merely tools for visual representation; they are catalysts for deeper learning and knowledge acquisition. Their benefits extend across various aspects of education, from individual learning to classroom instruction and beyond.
1. Strengthening Conceptual Understanding:
Concept maps promote a deeper understanding of concepts by revealing their interconnectedness and hierarchical relationships. By visualizing the connections between different ideas, learners can develop a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the subject matter.
2. Enhancing Memory and Recall:
The visual nature of concept maps aids in memory retention. The brain processes visual information more readily, allowing for easier recall of concepts and their relationships.
3. Facilitating Critical Thinking:
Concept mapping encourages critical thinking skills by prompting learners to analyze information, identify key concepts, and establish meaningful connections. This process fosters a deeper understanding of the subject matter and enhances problem-solving abilities.
4. Improving Communication and Collaboration:
Concept maps provide a common visual language for communication and collaboration. They facilitate shared understanding and allow learners to communicate their ideas effectively to others.
5. Supporting Assessment and Feedback:
Concept maps serve as valuable assessment tools, providing insights into student learning. By examining the connections and relationships represented in a student’s concept map, educators can gain a deeper understanding of their comprehension and identify areas needing further support.
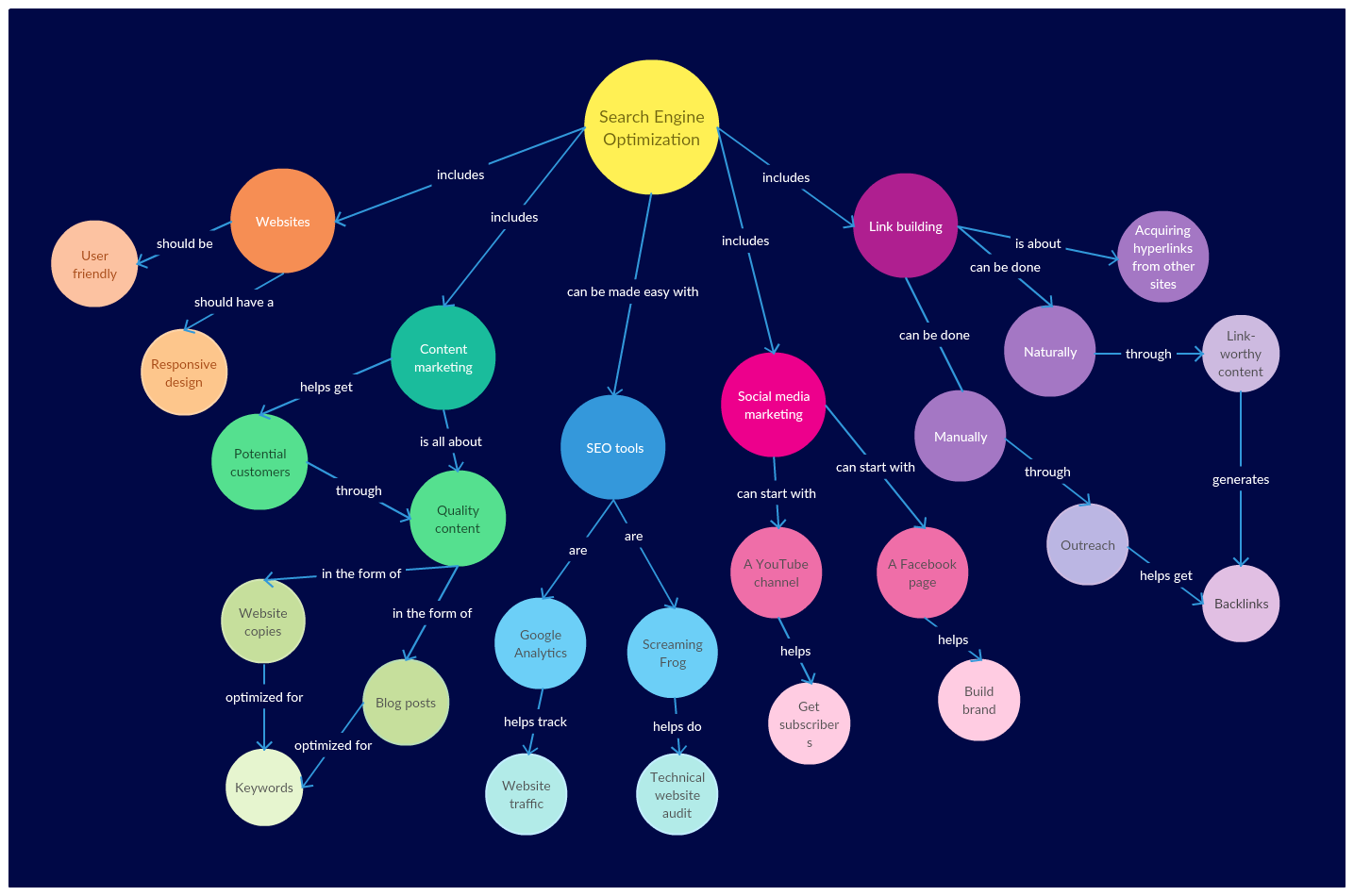
Applications of Education Concept Maps: A Wide Spectrum of Use Cases
The versatility of concept maps extends across various educational settings and disciplines. Here are some key applications:
1. Classroom Instruction:
- Pre-Lesson Activities: Concept maps can be used to activate prior knowledge, introduce new concepts, and set the stage for learning.
- During Lesson Activities: They can serve as visual organizers, guiding students through complex topics and facilitating discussions.
- Post-Lesson Activities: Concept maps can be used for summarizing learning, identifying gaps in understanding, and fostering reflection.
2. Individual Learning:
- Note-taking: Students can create concept maps to organize notes and capture key ideas from lectures, readings, and research.
- Study Guides: Concept maps serve as effective study guides, providing a visual overview of the subject matter and highlighting key relationships.
- Self-Assessment: Students can use concept maps to assess their understanding of a topic and identify areas requiring further study.
3. Collaborative Learning:
- Group Projects: Concept maps can be used to brainstorm ideas, organize tasks, and ensure shared understanding among group members.
- Peer Learning: Concept maps can facilitate peer learning by providing a visual framework for discussing concepts and sharing perspectives.
4. Curriculum Development:
- Unit Planning: Concept maps can be used to design curriculum units, outlining the key concepts and learning objectives.
- Assessment Design: Concept maps can inform the development of assessments that measure student understanding of the relationships between concepts.
5. Research and Development:
- Literature Reviews: Concept maps can be used to organize and synthesize information from research articles and other sources.
- Theory Building: Concept maps can be used to visualize and develop theoretical frameworks.
FAQs About Education Concept Maps: Addressing Common Queries
Q: How do I create a concept map?
A: Concept mapping involves a structured process:
- Identify the central concept: Define the main topic or idea.
- Brainstorm related concepts: Generate a list of concepts related to the central concept.
- Organize concepts hierarchically: Arrange concepts from general to specific, reflecting their relationships.
- Connect concepts with links: Draw lines or arrows between concepts, using linking words to clarify the nature of the relationship.
- Refine and revise: Review the map, ensuring clarity, accuracy, and logical flow.
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid when creating concept maps?
A:
- Overcrowding: Avoid cramming too many concepts onto a single map, which can hinder clarity.
- Vagueness: Use precise and specific terms in nodes, avoiding ambiguity.
- Unclear links: Ensure linking words or phrases clearly explain the relationship between concepts.
- Lack of hierarchy: Maintain a logical structure, organizing concepts from general to specific.
Q: What are some helpful tools for creating concept maps?
A: There are numerous software tools and online platforms available for creating concept maps:
- Mindomo: A cloud-based tool offering various features, including collaboration and sharing.
- Coggle: A simple and intuitive online tool for creating concept maps, flowcharts, and diagrams.
- FreeMind: A free, open-source software for creating mind maps and concept maps.
- XMind: A powerful tool for creating mind maps, concept maps, and other visual diagrams.
- Lucidchart: A versatile online diagramming tool that supports concept mapping and various other visual representations.
Q: Are concept maps suitable for all learners?
A: Concept maps can be adapted to suit different learning styles and preferences. While visual learners tend to benefit significantly, even learners with a preference for verbal or kinesthetic learning can find value in using concept maps.
Q: How can I incorporate concept maps into my teaching practice?
A: Here are some tips for integrating concept maps into your teaching:
- Start small: Introduce concept mapping gradually, beginning with simple topics.
- Model the process: Demonstrate how to create a concept map, explaining each step clearly.
- Provide guided practice: Offer opportunities for students to create concept maps collaboratively or individually, with your guidance and support.
- Provide feedback: Review student-created concept maps, offering constructive feedback on their structure, clarity, and accuracy.
- Make it fun: Incorporate games, activities, and technology to engage students and make concept mapping a more enjoyable experience.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Visual Learning
Concept maps offer a powerful and versatile approach to learning and teaching. By harnessing the benefits of visual representation and active engagement, concept maps empower learners to organize, understand, and retain knowledge more effectively.
Whether used for individual study, classroom instruction, or research endeavors, concept maps provide a valuable tool for navigating the complex landscape of knowledge and unlocking the full potential of learning.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Knowledge: A Comprehensive Guide to Education Concept Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!