Navigating The Australian Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To Regional Divisions
Navigating the Australian Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Regional Divisions
Related Articles: Navigating the Australian Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Regional Divisions
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Australian Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Regional Divisions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Australian Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Regional Divisions

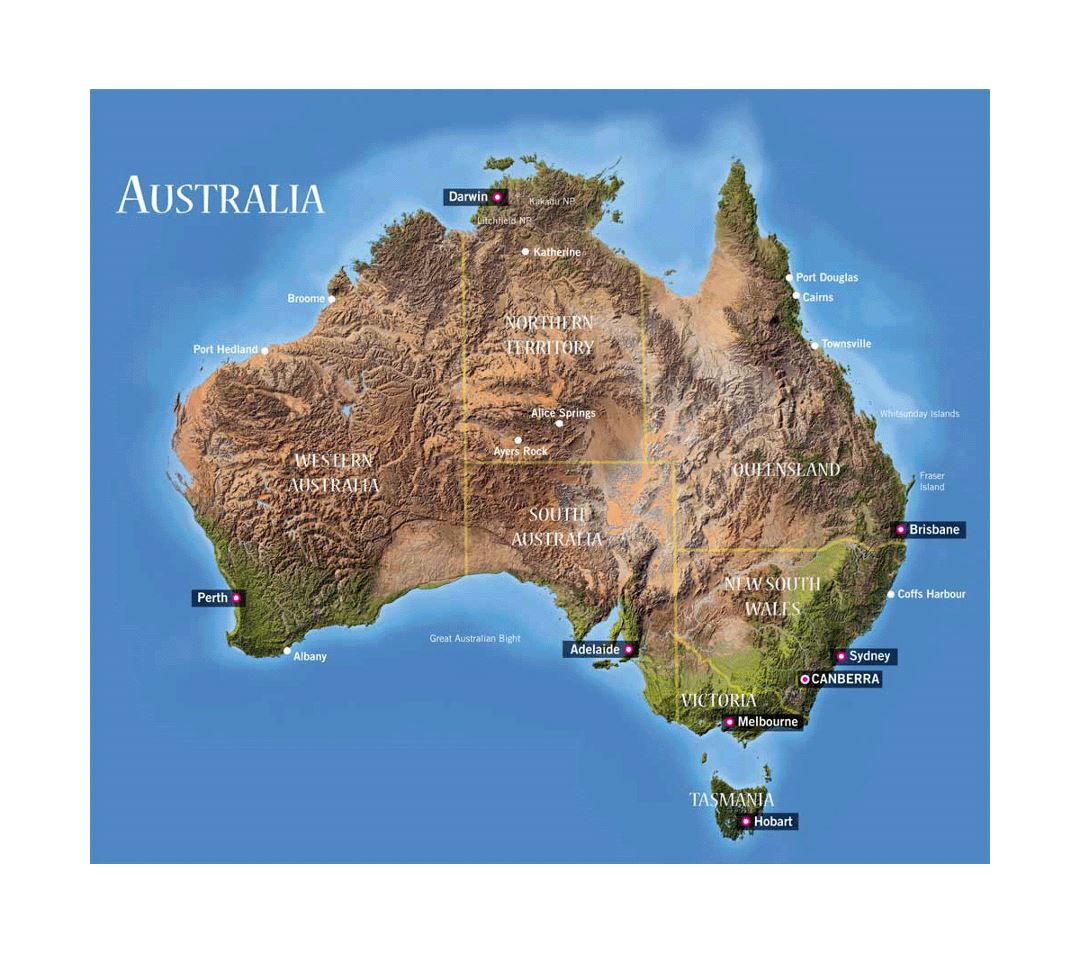
Australia, a vast and diverse continent, is often understood through its distinct regions. Understanding these regional divisions is crucial for appreciating the country’s unique geographical features, cultural tapestry, and economic landscape. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed exploration of Australia’s regions, encompassing their geographical characteristics, cultural nuances, and economic significance.
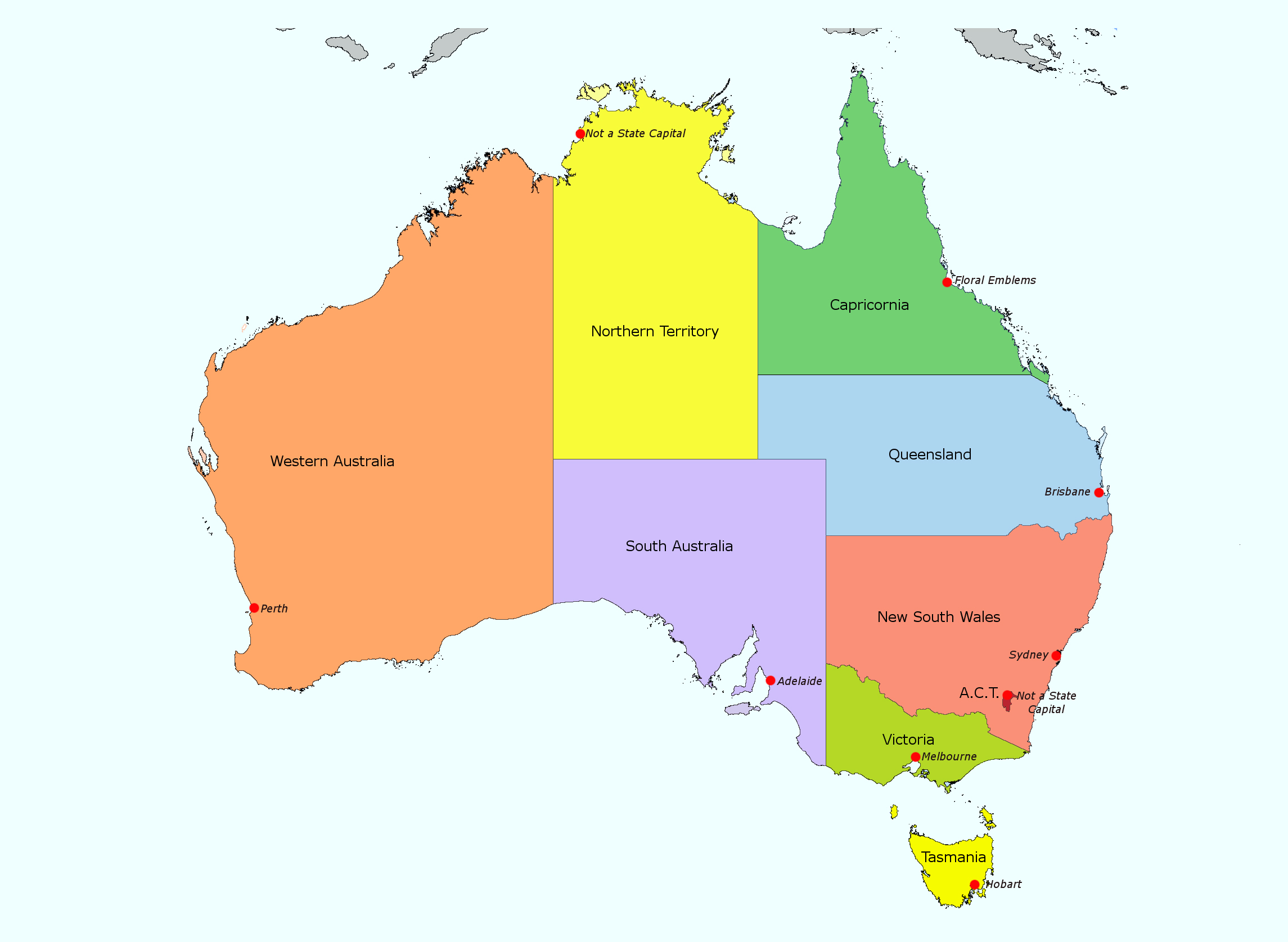
The Regional Divisions of Australia
Australia’s regional divisions are primarily defined by geographical, cultural, and economic factors. While different classifications exist, a commonly used framework categorizes the country into eight major regions:
1. Western Australia:
- Geography: Encompassing the entire western third of the continent, Western Australia boasts a vast and diverse landscape, ranging from the arid deserts of the interior to the lush forests of the southwest. It is home to the iconic Uluru (Ayers Rock), the world’s largest monolith, and the vast Pilbara region, rich in iron ore and other mineral resources.
- Culture: The region’s cultural identity is shaped by its indigenous heritage, European colonization, and a growing multicultural population. It boasts unique traditions, art forms, and festivals, reflecting its diverse cultural influences.
- Economy: Western Australia’s economy is heavily reliant on mining, particularly iron ore, gold, and nickel. Tourism, agriculture, and fisheries also play significant roles.
2. Northern Territory:
- Geography: Located in the north-central region of Australia, the Northern Territory is characterized by its vast desert landscapes, tropical rainforests, and the iconic Uluru-Kata Tjuta National Park. It is known for its rugged beauty and unique ecosystems.
- Culture: The Northern Territory is home to a rich indigenous culture, with strong ties to the land and traditional practices. It is also influenced by European colonization and a growing multicultural population.
- Economy: Tourism, mining, and cattle grazing are the dominant industries in the Northern Territory. The region’s unique landscapes and cultural heritage attract visitors from around the world.
3. South Australia:
- Geography: Situated in the southern central region of Australia, South Australia is known for its diverse landscapes, including the arid outback, the Flinders Ranges, and the coastal regions. It is home to the iconic Adelaide Hills and the vast Nullarbor Plain.
- Culture: South Australia boasts a vibrant cultural scene, with a strong focus on art, music, and food. The region is known for its winemaking industry, its unique culinary traditions, and its festivals.
- Economy: South Australia’s economy is driven by a range of sectors, including mining, agriculture, manufacturing, and tourism. The region is a major producer of wine, wheat, and other agricultural products.
4. Queensland:
- Geography: Located in the northeast of Australia, Queensland is known for its stunning coastline, the Great Barrier Reef, and its diverse landscapes, which range from tropical rainforests to arid deserts. It is home to the iconic Gold Coast and the Sunshine Coast.
- Culture: Queensland’s culture is a blend of indigenous traditions, European influences, and a vibrant surf culture. The region is known for its laid-back lifestyle, its outdoor activities, and its festivals.
- Economy: Queensland’s economy is driven by tourism, mining, agriculture, and manufacturing. The region is a major producer of coal, sugar, and other agricultural products.
5. New South Wales:
- Geography: Situated on the east coast of Australia, New South Wales is known for its diverse landscapes, including the Blue Mountains, the Hunter Valley, and the coastal regions. It is home to the iconic Sydney Harbour and the city of Sydney, the country’s largest metropolis.
- Culture: New South Wales is a cultural hub, with a rich history, a vibrant arts scene, and a diverse population. The region is known for its world-class museums, theaters, and galleries.
- Economy: New South Wales’s economy is driven by a wide range of sectors, including finance, tourism, manufacturing, and agriculture. The region is a major producer of wine, wool, and other agricultural products.
6. Victoria:
- Geography: Located in the southeast of Australia, Victoria is known for its diverse landscapes, including the Great Dividing Range, the Victorian Alps, and the coastal regions. It is home to the iconic Melbourne, the country’s second-largest city.
- Culture: Victoria is a cultural powerhouse, with a strong focus on the arts, music, and sport. The region is known for its festivals, its vibrant nightlife, and its multicultural population.
- Economy: Victoria’s economy is driven by a range of sectors, including finance, manufacturing, tourism, and education. The region is a major producer of wine, wool, and other agricultural products.
7. Tasmania:
- Geography: An island state located off the southeast coast of Australia, Tasmania is known for its rugged landscapes, including the Tasmanian Wilderness World Heritage Area, the Cradle Mountain-Lake St Clair National Park, and the Freycinet National Park.
- Culture: Tasmania boasts a unique cultural identity, with a strong connection to its indigenous heritage and its colonial past. The region is known for its art, music, and its distinctive food and wine.
- Economy: Tasmania’s economy is driven by a range of sectors, including tourism, agriculture, and forestry. The region is a major producer of apples, potatoes, and other agricultural products.
8. Australian Capital Territory (ACT):
- Geography: Located in the southeastern part of Australia, the Australian Capital Territory (ACT) is home to Canberra, the country’s capital city. It is a small territory with a diverse landscape, including the Brindabella Ranges and the Murrumbidgee River.
- Culture: The ACT is known for its cultural institutions, including the National Gallery of Australia, the National Library of Australia, and the Australian War Memorial. The region also boasts a vibrant arts scene and a diverse population.
- Economy: The ACT’s economy is driven by government services, education, and tourism. The region is a major center for research and development.
Benefits of Understanding Australia’s Regional Divisions
Understanding Australia’s regional divisions offers several benefits:
- Enhanced Geographic Awareness: It provides a comprehensive understanding of the country’s vast and diverse landscapes, including its unique ecosystems, geological formations, and climatic variations.
- Cultural Appreciation: It fosters an appreciation for the rich cultural tapestry of Australia, encompassing indigenous traditions, colonial influences, and multicultural diversity.
- Economic Insight: It sheds light on the economic drivers of each region, highlighting key industries, resource distribution, and regional economic strengths.
- Travel Planning: It assists travelers in planning their trips, enabling them to choose destinations that align with their interests and preferences.
- Informed Decision-Making: It empowers individuals and organizations to make informed decisions about investments, business ventures, and social initiatives.
FAQs about Australia’s Regional Divisions
Q: What are the key factors that define Australia’s regional divisions?
A: Australia’s regional divisions are primarily defined by geographical, cultural, and economic factors. These include:
- Geography: Landscapes, climate, natural resources, and geographical features.
- Culture: Indigenous heritage, colonial influences, multicultural diversity, and local traditions.
- Economy: Key industries, resource distribution, economic strengths, and employment patterns.
Q: How do the regional divisions influence Australia’s cultural landscape?
A: Each region has its unique cultural identity, shaped by its history, demographics, and local traditions. Indigenous cultures, European influences, and multicultural diversity have all contributed to the rich tapestry of Australian culture.
Q: What are the economic implications of Australia’s regional divisions?
A: The regional divisions reflect the economic strengths and challenges of different parts of the country. Each region has its unique economic drivers, ranging from mining and agriculture to tourism and manufacturing.
Q: How can understanding Australia’s regional divisions benefit travelers?
A: It allows travelers to plan their trips based on their interests and preferences. They can choose destinations that align with their desire to explore specific landscapes, experience different cultures, or engage in particular activities.
Q: Are there any other classifications used to define Australia’s regions?
A: Yes, other classifications exist, such as the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) regional divisions, which are used for statistical purposes. These classifications may differ slightly from the commonly used framework outlined in this guide.
Tips for Exploring Australia’s Regions
- Research: Thoroughly research the specific regions you plan to visit, understanding their unique characteristics, attractions, and cultural nuances.
- Embrace Local Culture: Engage with local communities, learn about their traditions, and appreciate the region’s cultural identity.
- Respect the Environment: Be mindful of your impact on the environment and practice sustainable travel practices.
- Consider the Season: Plan your trip during the most favorable season for each region, taking into account weather conditions and seasonal activities.
- Explore Beyond Major Cities: Venture beyond major cities to discover the hidden gems and unique experiences offered by each region.
Conclusion
Understanding Australia’s regional divisions is crucial for appreciating the country’s vast and diverse landscape, its rich cultural tapestry, and its economic landscape. From the arid deserts of the interior to the lush rainforests of the east coast, each region offers unique experiences, cultural insights, and economic opportunities. By exploring these regional divisions, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of this extraordinary continent and its multifaceted character.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Australian Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Regional Divisions. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!