Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to Japan’s Geography
Related Articles: Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to Japan’s Geography
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to Japan’s Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to Japan’s Geography

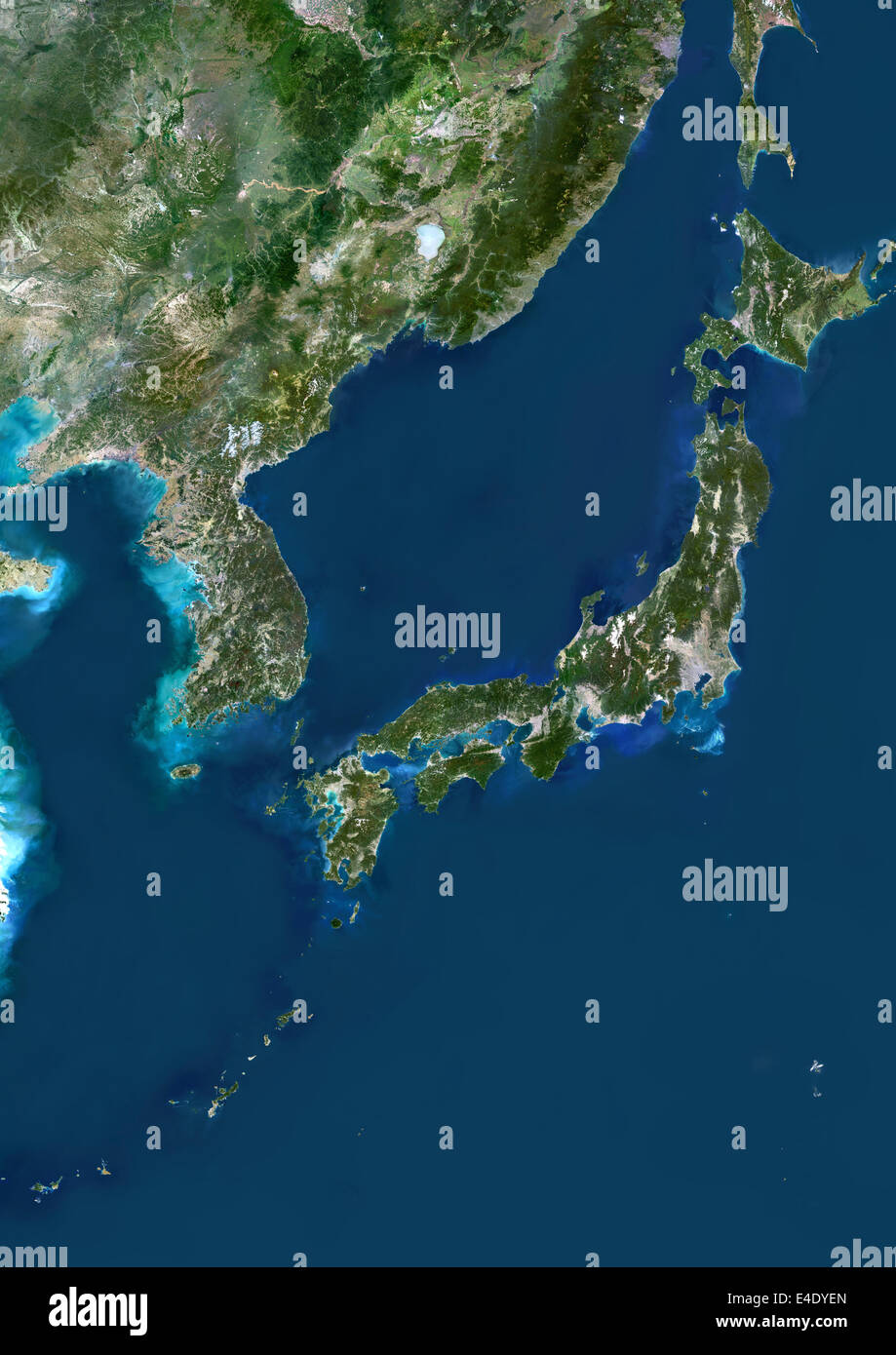
Japan, an island nation in East Asia, is a captivating tapestry of diverse landscapes, rich history, and vibrant culture. Its geographical location, a chain of four main islands and thousands of smaller ones, has shaped its identity and played a pivotal role in its development. Understanding the intricate geography of Japan is crucial for appreciating its unique character and its role in the global context.
The Archipelago’s Formation:
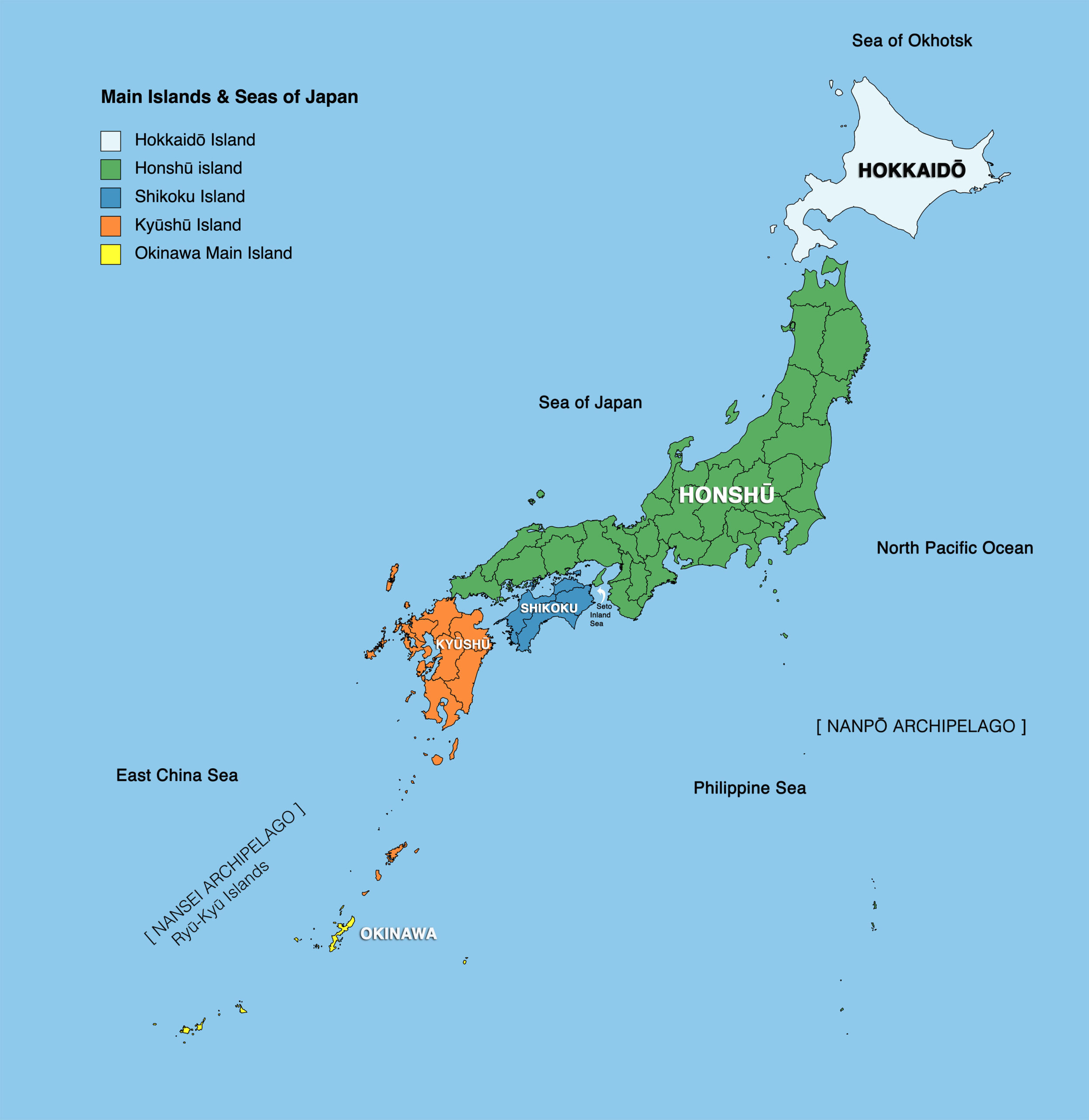
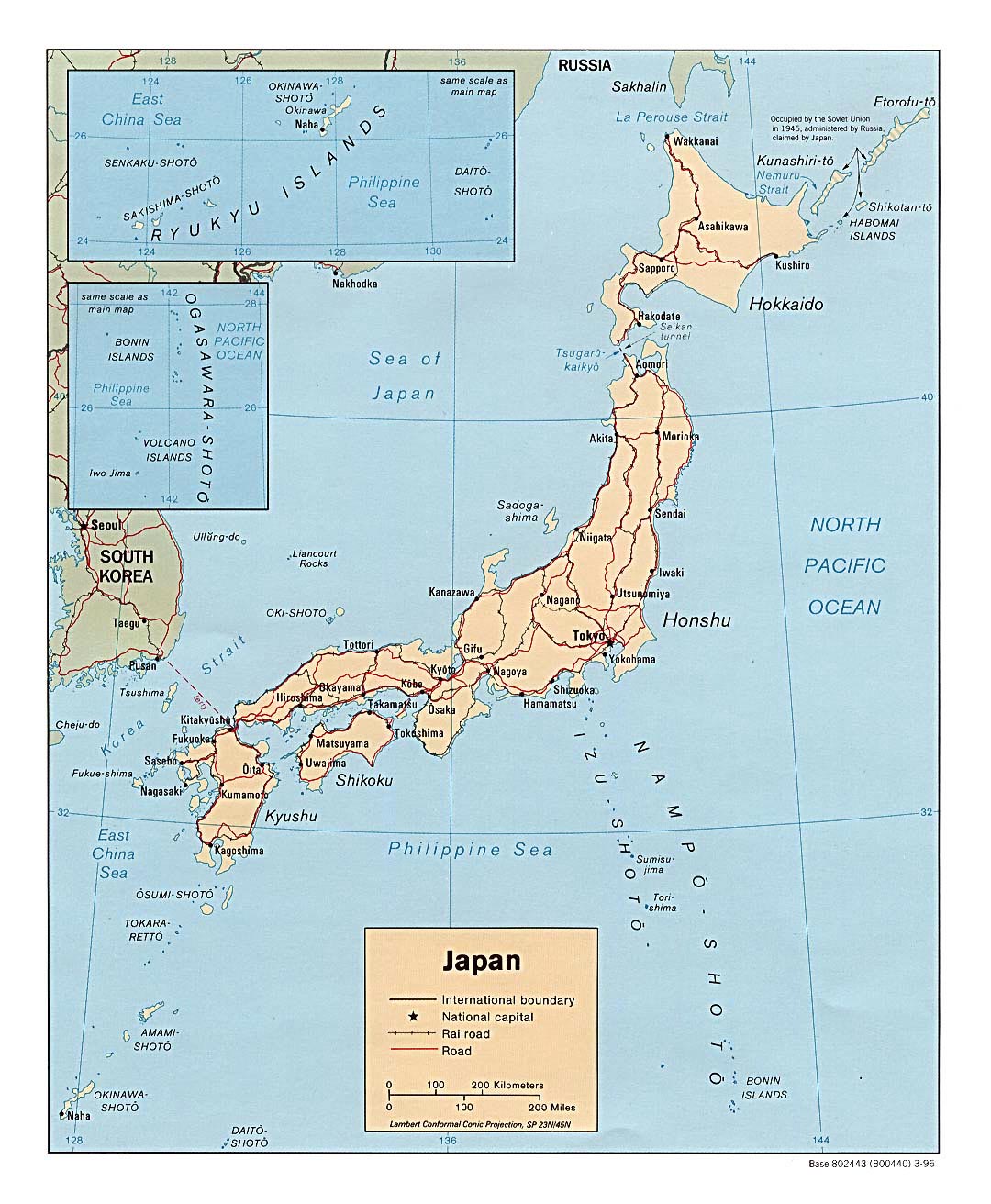
Japan’s islands emerged from the fiery depths of the Earth, formed by volcanic activity along the Pacific Ring of Fire. This geological process continues to shape the landscape, with active volcanoes and frequent earthquakes defining the country’s natural environment. The four main islands, Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu, are separated by narrow straits and interconnected by bridges and tunnels, creating a complex and dynamic network.
Island by Island: A Detailed Exploration
Hokkaido: The northernmost island, Hokkaido, is known for its vast wilderness, pristine mountains, and abundant wildlife. It is home to Mount Asahi, the highest peak on the island, and the Shiretoko Peninsula, a UNESCO World Heritage site. Hokkaido is also a major agricultural region, producing dairy products, seafood, and vegetables.
Honshu: The largest and most populous island, Honshu, is a diverse landscape encompassing towering mountains, fertile plains, and bustling cities. It is home to Mount Fuji, Japan’s iconic symbol, and the capital city, Tokyo, a global metropolis. Honshu is also home to the ancient capital city of Kyoto, known for its rich cultural heritage.
Shikoku: The smallest of the four main islands, Shikoku, is known for its lush forests, pilgrimage routes, and stunning coastal scenery. It is home to the famous Shikoku 88 Temple Pilgrimage, a spiritual journey that attracts thousands of visitors annually.
Kyushu: The southernmost island, Kyushu, is characterized by its volcanic landscapes, hot springs, and subtropical climate. It is home to Mount Aso, one of Japan’s most active volcanoes, and the city of Fukuoka, a major economic and cultural center.
The Islands Beyond:
Beyond the four main islands, Japan boasts thousands of smaller islands, many of which are uninhabited. These islands offer a glimpse into the country’s diverse ecosystems, from the volcanic islands of the Izu archipelago to the subtropical islands of the Ryukyu archipelago.
Geographical Significance:
Japan’s geographical location has profoundly influenced its history, culture, and development. Its island nature has fostered a unique sense of national identity and fostered a resilient spirit, as the nation has faced numerous challenges throughout its history. Its proximity to the Asian mainland has facilitated trade and cultural exchange, shaping its economic and social development.
The Importance of Understanding Japan’s Geography:
For travelers, understanding Japan’s geography is essential for planning itineraries and appreciating the diverse landscapes and cultural experiences the country offers. For business professionals, understanding the geographical factors influencing economic activity and infrastructure development is crucial for making informed decisions. And for anyone interested in the world’s history and culture, Japan’s geographical context provides a valuable lens for understanding its unique story.
FAQs about Japan’s Geography:
1. What is the highest mountain in Japan?
Mount Fuji, located on Honshu island, is the highest mountain in Japan, reaching a height of 3,776 meters (12,388 feet).
2. How many active volcanoes are there in Japan?
Japan has over 100 active volcanoes, a testament to its location on the Pacific Ring of Fire.
3. What is the largest island in Japan?
Honshu is the largest island in Japan, covering over 230,000 square kilometers (89,000 square miles).
4. What is the capital city of Japan?
Tokyo, located on Honshu island, is the capital city of Japan.
5. How many islands are there in Japan?
Japan is composed of over 6,800 islands, with four main islands and thousands of smaller ones.
Tips for Exploring Japan’s Geography:
- Plan your itinerary based on your interests: Do you want to explore the mountains of Hokkaido, the cultural treasures of Kyoto, or the volcanic landscapes of Kyushu?
- Utilize public transportation: Japan’s extensive and efficient public transportation system makes it easy to travel between islands and explore different regions.
- Embrace the local culture: Immerse yourself in the unique customs and traditions of each region.
- Respect the environment: Japan is a country with a strong connection to nature, so be mindful of the environment and leave no trace.
Conclusion:
Japan’s geography is a captivating and dynamic element of its identity. From the volcanic peaks of Hokkaido to the subtropical shores of Kyushu, the archipelago offers a diverse range of landscapes and experiences. Understanding the geographical context is crucial for appreciating the country’s rich history, culture, and development. By exploring the islands and their unique characteristics, visitors can gain a deeper understanding of this fascinating and multifaceted nation.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to Japan’s Geography. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!