Mount Fuji: A Majestic Icon on the Map of Japan
Related Articles: Mount Fuji: A Majestic Icon on the Map of Japan
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mount Fuji: A Majestic Icon on the Map of Japan. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mount Fuji: A Majestic Icon on the Map of Japan

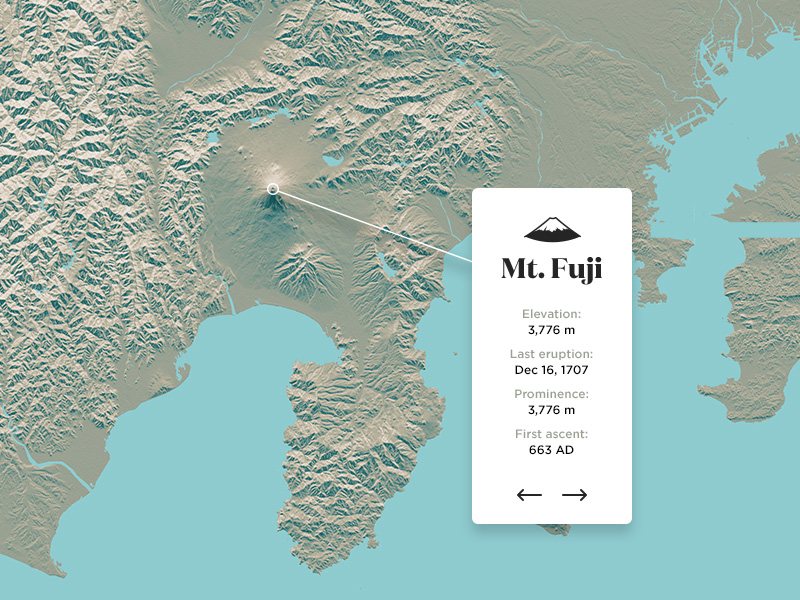
Mount Fuji, Japan’s iconic stratovolcano, dominates the landscape of central Honshu Island. This majestic peak, reaching a height of 3,776 meters (12,388 feet), is a symbol of Japan, often depicted in art, literature, and photography. Its snow-capped summit, visible from Tokyo on clear days, holds a powerful presence in the Japanese cultural landscape.
Geographical Significance:
Mount Fuji is located within the Fuji-Hakone-Izu National Park, approximately 100 kilometers southwest of Tokyo. Its location on the border of Yamanashi and Shizuoka prefectures places it within a region characterized by volcanic activity. The mountain itself is a stratovolcano, formed by layers of solidified lava and ash from successive eruptions. Its last eruption occurred in 1707, and while dormant, it is considered an active volcano.
Cultural Importance:
Mount Fuji holds immense cultural significance in Japan. It is revered as a sacred mountain, a place of pilgrimage and spiritual practice. The mountain is associated with Shintoism, a native Japanese religion that worships nature spirits. Numerous shrines and temples dot the mountain’s slopes, testament to its religious importance.
Beyond religion, Mount Fuji is a source of inspiration for artists, poets, and writers. Its beauty has been immortalized in countless works of art, including woodblock prints, paintings, and poetry. The iconic image of Mount Fuji, often depicted with its snow-capped peak and symmetrical cone shape, has become a symbol of Japan’s natural beauty and cultural identity.
Climbing Mount Fuji:
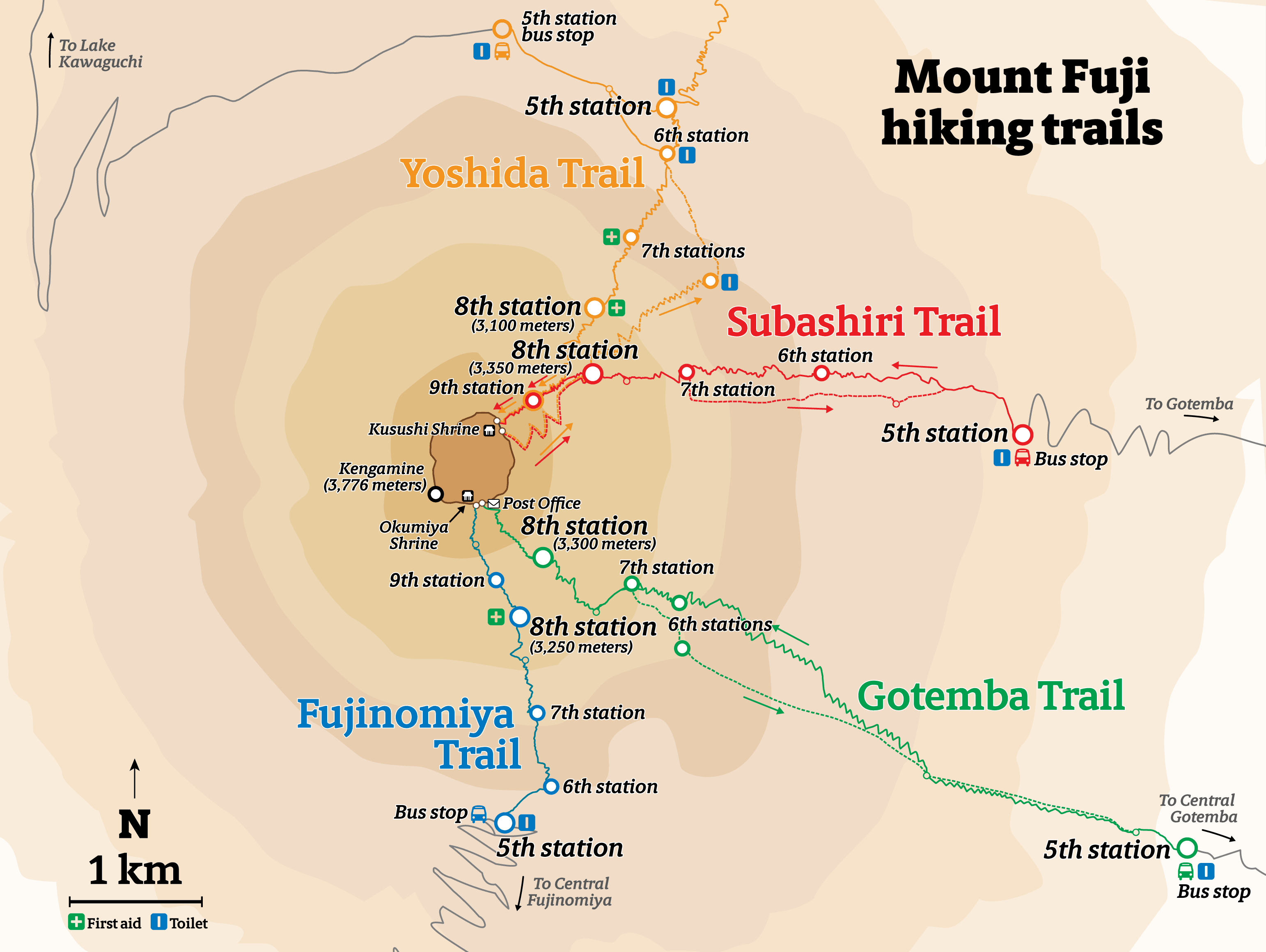
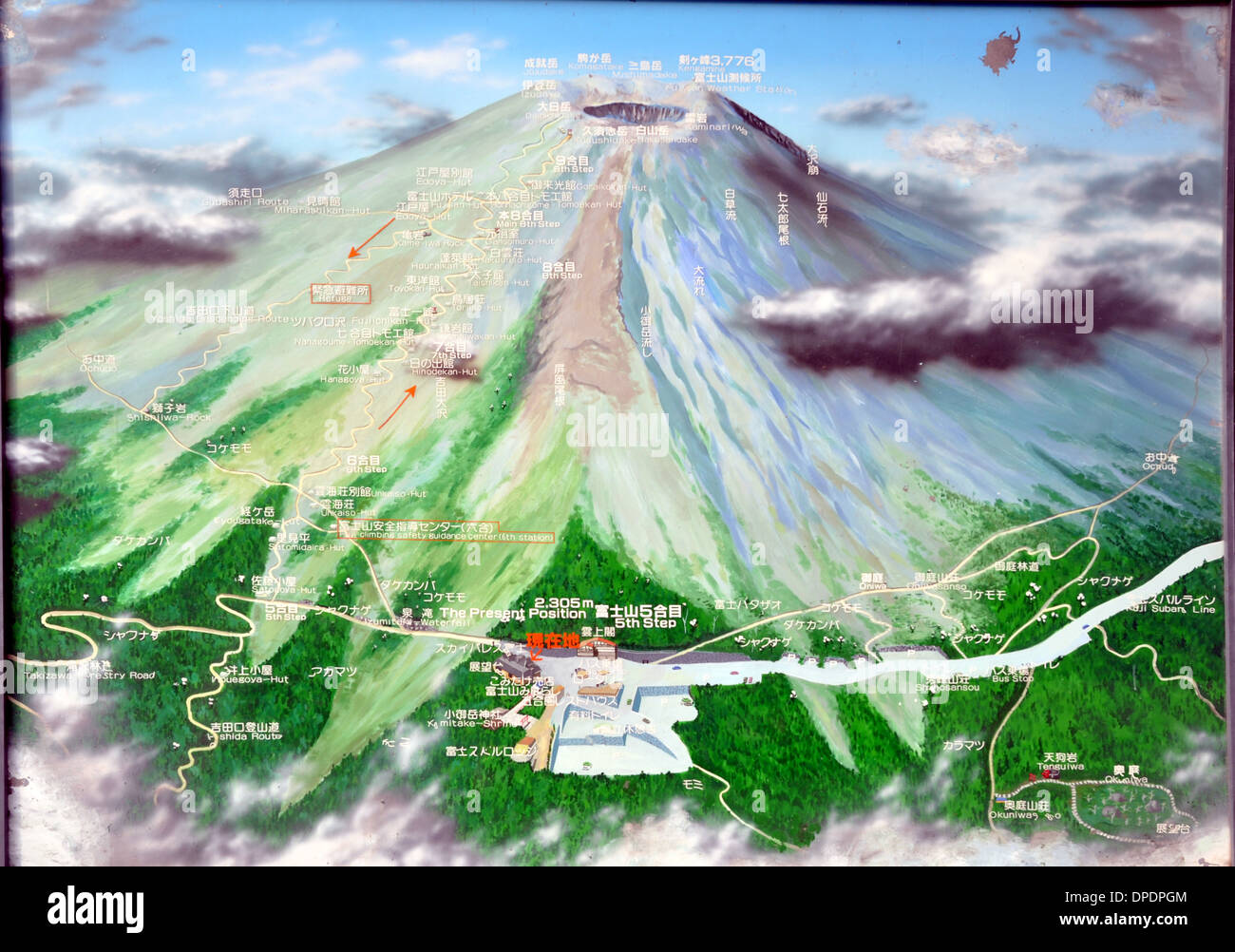
Mount Fuji is a popular destination for climbers from around the world. The climbing season typically runs from July to September, when the weather is most favorable. The mountain offers various climbing routes, with the most popular being the Yoshida Trail, which starts at the fifth station.
While the ascent is challenging, the reward is breathtaking. The summit offers panoramic views of the surrounding countryside, including the Pacific Ocean and the Japanese Alps. Climbers can witness stunning sunrises and sunsets from the peak, making the journey truly unforgettable.
Environmental Significance:
Mount Fuji’s unique ecosystem supports a diverse range of flora and fauna. The mountain’s lower slopes are covered in dense forests, home to various species of trees, including Japanese cedar, Japanese cypress, and Japanese beech. Higher up, the vegetation transitions to alpine meadows, where hardy plants thrive in the harsh conditions.
The mountain’s unique environment also supports a variety of animal life, including monkeys, deer, and birds. The surrounding national park plays a crucial role in preserving this fragile ecosystem, ensuring the continued health of Mount Fuji and its biodiversity.
Tourism and Economy:
Mount Fuji is a major tourist attraction, drawing millions of visitors annually. The surrounding area offers various attractions, including hot springs, museums, and hiking trails. The tourism industry associated with Mount Fuji contributes significantly to the local economy, supporting hotels, restaurants, and other businesses.
Challenges and Conservation:
Mount Fuji faces several challenges, including increasing tourism pressure, climate change, and pollution. The mountain’s fragile ecosystem is susceptible to damage from overuse, litter, and the impact of human activities.
Conservation efforts are underway to protect Mount Fuji’s natural beauty and cultural significance. The government and local communities are working together to promote responsible tourism, reduce pollution, and mitigate the impact of climate change.
FAQs about Mount Fuji:
Q: What is the best time to climb Mount Fuji?
A: The climbing season for Mount Fuji typically runs from July to September when the weather is most favorable.
Q: How long does it take to climb Mount Fuji?
A: The time it takes to climb Mount Fuji varies depending on the route and the climber’s fitness level. Most climbers take one to two days to reach the summit and descend.
Q: Is it dangerous to climb Mount Fuji?
A: Climbing Mount Fuji can be challenging and requires physical fitness and proper preparation. The weather conditions on the mountain can change quickly, and altitude sickness is a potential risk.
Q: What are the best things to see around Mount Fuji?
A: The surrounding area offers various attractions, including the Fuji Five Lakes, the Hakone National Park, and the Aokigahara Forest.
Q: How can I get to Mount Fuji?
A: Mount Fuji is easily accessible by train or bus from Tokyo. Several bus lines operate between Tokyo and the mountain’s base.
Tips for Visiting Mount Fuji:
- Plan ahead: Research the climbing routes, weather conditions, and necessary equipment before your trip.
- Be prepared: Pack warm clothing, rain gear, and sturdy hiking boots.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout your climb.
- Acclimatize: Spend some time at a lower altitude before attempting a summit climb.
- Respect the mountain: Leave no trace behind and dispose of trash properly.
Conclusion:
Mount Fuji is a natural wonder and a cultural icon that holds a special place in the hearts of the Japanese people. Its majestic presence, stunning beauty, and cultural significance make it a must-visit destination for travelers from around the world. By understanding its geographical, cultural, and environmental importance, visitors can appreciate the multifaceted nature of this iconic mountain and contribute to its preservation for future generations.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mount Fuji: A Majestic Icon on the Map of Japan. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!