Exploring The West Coast Of America: A Journey Through Geography, Culture, And History
Exploring the West Coast of America: A Journey Through Geography, Culture, and History
Related Articles: Exploring the West Coast of America: A Journey Through Geography, Culture, and History
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Exploring the West Coast of America: A Journey Through Geography, Culture, and History. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Exploring the West Coast of America: A Journey Through Geography, Culture, and History

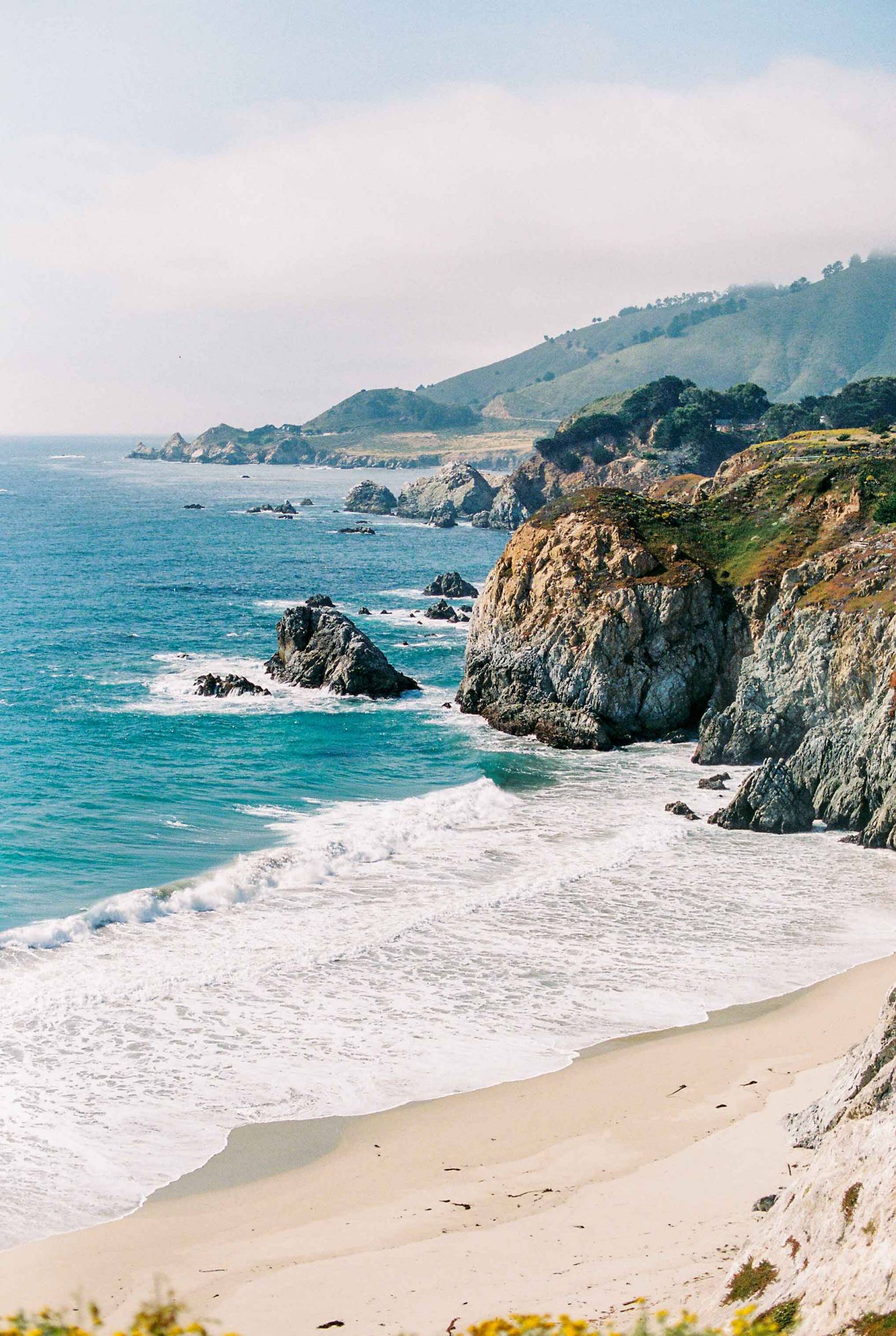
The West Coast of America, a region encompassing the Pacific coast of the United States and Canada, is a tapestry of diverse landscapes, vibrant cultures, and significant historical events. Its geographical features, from towering mountain ranges to sun-drenched beaches, have shaped its unique identity and played a pivotal role in the development of both nations. This article delves into the intricacies of the West Coast, exploring its geography, history, culture, and the factors that make it a captivating destination for exploration and understanding.
Geography: A Coast of Contrasts
The West Coast is characterized by a striking contrast of geographical features, creating a landscape of breathtaking beauty and diverse ecosystems.
-
The Pacific Coast: The defining feature of the West Coast is the Pacific Ocean, which stretches for thousands of miles, influencing the region’s climate, economy, and culture. Its vastness has inspired countless artists and writers, and its waves have attracted surfers and adventurers for generations.
-
The Cascade Range: A chain of volcanic mountains, the Cascades extend from northern California to British Columbia, creating a dramatic backdrop to the region. Mount Rainier, Mount Shasta, and Mount Hood are among its most prominent peaks, drawing climbers and outdoor enthusiasts.
-
The Sierra Nevada: This mountain range, known for its granite peaks and deep canyons, is home to Yosemite National Park, a natural wonder renowned for its towering granite cliffs, cascading waterfalls, and giant sequoia trees.
-
The Coast Ranges: A series of lower mountains parallel to the Pacific Coast, the Coast Ranges are characterized by rolling hills, dense forests, and fertile valleys, contributing to the region’s agricultural abundance.
-
The Great Basin: A vast, arid region east of the Sierra Nevada, the Great Basin is characterized by high plateaus, salt flats, and desert landscapes. It is home to unique ecosystems, including the Mojave Desert, known for its Joshua trees and cacti.
History: From Exploration to Innovation
The history of the West Coast is marked by exploration, settlement, and innovation.
-
Early Exploration: European explorers, including Spanish conquistadors and British seafarers, were drawn to the West Coast by its potential for trade and resources. The Spanish established missions and settlements in California, while the British explored the coast of what is now British Columbia.
-
The Gold Rush: The discovery of gold in California in 1848 triggered a massive influx of people, transforming the region from a sparsely populated frontier into a booming center of economic activity. This period witnessed rapid growth, urbanization, and social change.
-
The Pacific Northwest: The Pacific Northwest, encompassing Washington, Oregon, and British Columbia, developed a distinct identity based on logging, fishing, and agriculture. The region also became a hub for technological innovation, particularly in the aerospace and software industries.
-
The California Dream: California, with its sunny climate, diverse landscapes, and entrepreneurial spirit, has long been a symbol of opportunity and a magnet for migrants. The state’s booming economy, fueled by technology, entertainment, and agriculture, has shaped the West Coast’s cultural and economic landscape.
Culture: A Mosaic of Influences
The West Coast is a melting pot of cultures, reflecting its diverse history and immigration patterns.
-
Native American Cultures: Indigenous peoples have inhabited the West Coast for millennia, leaving a rich legacy of languages, traditions, and art. From the Coast Salish of British Columbia to the Chumash of California, their cultures have shaped the region’s identity.
-
Hispanic Influence: The Spanish presence in California left a lasting mark on the region’s language, cuisine, and architecture. From the Spanish missions to the vibrant Mexican culture of Southern California, Hispanic influences are woven into the fabric of the West Coast.
-
Asian Influences: The West Coast has been a destination for Asian immigrants for centuries, contributing to the region’s cultural diversity. From the Chinese communities of San Francisco to the Japanese gardens of Seattle, Asian influences are visible in cuisine, art, and architecture.
-
Bohemian Spirit: The West Coast has a reputation for its bohemian spirit, attracting artists, writers, and musicians seeking creative freedom and inspiration. From the Beat Generation in San Francisco to the grunge scene in Seattle, the West Coast has been a breeding ground for artistic movements.
Importance and Benefits
The West Coast holds immense importance due to its diverse natural resources, thriving economy, and cultural significance.
-
Economic Engine: The West Coast is home to major industries, including technology, entertainment, agriculture, and tourism. Silicon Valley, Hollywood, and the agricultural heartland of California are all located on the West Coast, contributing significantly to the U.S. economy.
-
Environmental Significance: The West Coast is a critical region for biodiversity conservation, with numerous national parks, forests, and marine sanctuaries protecting its diverse ecosystems. The region also faces environmental challenges, including climate change and pollution, highlighting the importance of sustainable practices.
-
Cultural Hub: The West Coast is a center for cultural expression, attracting artists, writers, musicians, and performers from around the world. Its vibrant arts scene, from theater and dance to music and film, contributes to its reputation as a dynamic and innovative region.
FAQs
Q: What are the major cities on the West Coast of America?
A: Major cities on the West Coast include:
- United States: San Francisco, Los Angeles, Seattle, Portland, San Diego, Vancouver, and Phoenix.
- Canada: Vancouver, Victoria, and Nanaimo.
Q: What are the most popular tourist destinations on the West Coast?
A: Some of the most popular tourist destinations on the West Coast include:
- California: Yosemite National Park, Disneyland, Hollywood, San Francisco Golden Gate Bridge, Alcatraz Island, Death Valley National Park, and the Pacific Coast Highway.
- Oregon: Crater Lake National Park, Oregon Coast, and Columbia River Gorge.
- Washington: Mount Rainier National Park, Olympic National Park, and Seattle Space Needle.
- British Columbia: Vancouver Island, Banff National Park, and Whistler Blackcomb.
Q: What is the climate like on the West Coast?
A: The West Coast experiences a wide range of climates, influenced by the Pacific Ocean and the mountain ranges.
- Northern California and the Pacific Northwest: Generally mild and wet, with cool summers and rainy winters.
- Southern California: Mediterranean climate with warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters.
- Great Basin: Arid and semi-arid, with hot summers and cold winters.
Q: What are some of the major industries on the West Coast?
A: Major industries on the West Coast include:
- Technology: Silicon Valley, located in California, is a global hub for technology innovation, home to companies like Apple, Google, and Facebook.
- Entertainment: Hollywood, also in California, is the center of the American film and television industry.
- Agriculture: California is known for its agricultural abundance, producing fruits, vegetables, and nuts for the nation.
- Tourism: The West Coast is a popular tourist destination, drawing visitors to its natural beauty, cultural attractions, and outdoor activities.
Tips
- Plan your trip: The West Coast is a vast region, so plan your itinerary carefully to maximize your time and experience.
- Pack appropriately: The climate varies greatly, so pack layers and be prepared for different weather conditions.
- Rent a car: A car is essential for exploring the diverse landscapes and attractions of the West Coast.
- Take advantage of outdoor activities: The West Coast offers a wide range of outdoor activities, from hiking and biking to kayaking and surfing.
- Embrace the culture: The West Coast is a melting pot of cultures, so take the opportunity to experience its diverse cuisine, art, and music.
Conclusion
The West Coast of America is a region of exceptional beauty, cultural richness, and historical significance. Its diverse landscapes, thriving economy, and vibrant culture make it a captivating destination for exploration and understanding. From the towering mountains of the Cascades to the sun-drenched beaches of California, the West Coast offers a unique blend of natural wonders, cultural experiences, and historical landmarks. As a region that has played a crucial role in shaping the history and identity of both the United States and Canada, the West Coast continues to be a source of inspiration and innovation, attracting visitors and residents alike.
![Exploration: Lewis and Clark [ushistory.org]](https://www.ushistory.org/us/images/lewclark.jpg)






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Exploring the West Coast of America: A Journey Through Geography, Culture, and History. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!