Demystifying the Running Mile Map: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Demystifying the Running Mile Map: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Demystifying the Running Mile Map: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Demystifying the Running Mile Map: A Comprehensive Guide
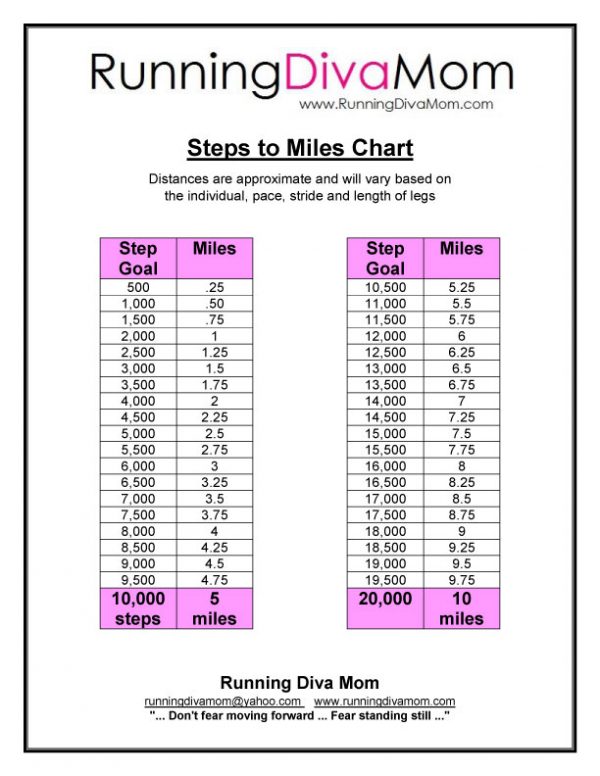
For runners of all levels, the mile map is a powerful tool that can elevate training and performance. This detailed guide explores the intricacies of mile maps, their benefits, and how to effectively utilize them.
Understanding the Mile Map: A Visual Representation of Distance
A mile map is a visual representation of a running route, typically broken down into mile markers. These markers can be physical signs placed along the route, or digitally represented on a map application. Each mile marker indicates the completion of a specific distance, providing runners with a clear visual reference point for their progress.
Benefits of Using Mile Maps in Running:
- Enhanced Pace Control: Mile maps enable runners to track their pace throughout the run. By observing the time spent on each mile, runners can identify areas where they need to adjust their pace to maintain consistency or achieve specific goals. This information is particularly valuable for interval training or races, where maintaining a consistent pace is crucial.
- Improved Motivation and Goal Setting: Observing progress on a mile map can be a powerful motivator. Knowing the distance covered and the miles remaining can inspire runners to push harder and stay focused on their goals. Mile markers serve as tangible reminders of the journey, making each mile feel more achievable.
- Increased Efficiency and Strategy: Mile maps facilitate strategic planning for runs. Runners can identify challenging sections or potential bottlenecks on a route, allowing them to adjust their strategy accordingly. For example, knowing the location of a steep hill can prompt runners to conserve energy before the ascent.
- Enhanced Safety: Mile maps provide runners with a clear understanding of the route, minimizing the risk of getting lost. This is especially important for runners exploring unfamiliar areas or participating in races. The markers can serve as reassuring landmarks, offering a sense of security and direction.
Types of Mile Maps:
- Physical Mile Markers: These are physical signs placed at each mile interval along a running route. They are typically found on popular running trails, race courses, or designated running paths.
- Digital Mile Maps: These are digital representations of routes displayed on map applications or GPS devices. They often include mile markers, elevation profiles, and other relevant information. Popular applications like Strava, Runkeeper, or Google Maps offer this functionality.
Creating and Using Mile Maps Effectively:
- Choose a Suitable Route: Select a route that aligns with your training goals and fitness level. Consider factors like distance, terrain, and traffic conditions.
- Identify Mile Markers: Use physical markers, map applications, or other tools to mark each mile on the route.
- Track Time and Pace: Record the time spent on each mile to assess your pace and identify areas for improvement.
- Analyze and Adjust: Regularly review your mile map data to identify patterns and adjust your training strategy accordingly.
FAQs about Mile Maps:
Q: Are mile maps necessary for all runners?
A: While not strictly necessary for all runners, mile maps can be particularly beneficial for those focused on improving pace, achieving specific goals, or exploring new routes.
Q: How accurate are digital mile maps?
A: The accuracy of digital mile maps depends on the quality of the data used and the reliability of the GPS signal. Some applications may provide more accurate data than others.
Q: Can mile maps be used for other activities like cycling or hiking?
A: Yes, mile maps can be used for any activity where distance is a key factor. Many map applications offer mile markers for various activities.
Tips for Utilizing Mile Maps:
- Use a Consistent Method: Stick to one method of tracking mile markers to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Consider Elevation: Factor in elevation changes when analyzing pace and effort.
- Focus on Progress: Use mile maps to celebrate progress and stay motivated.
- Experiment and Adjust: Don’t be afraid to experiment with different mile map methods and adjust your approach based on your needs.
Conclusion:
Mile maps are valuable tools for runners seeking to enhance their training, improve performance, and achieve their goals. By providing a visual representation of distance, they empower runners to track progress, control pace, and strategize effectively. Whether utilizing physical markers or digital applications, incorporating mile maps into your running routine can significantly contribute to a more enjoyable and successful running experience.

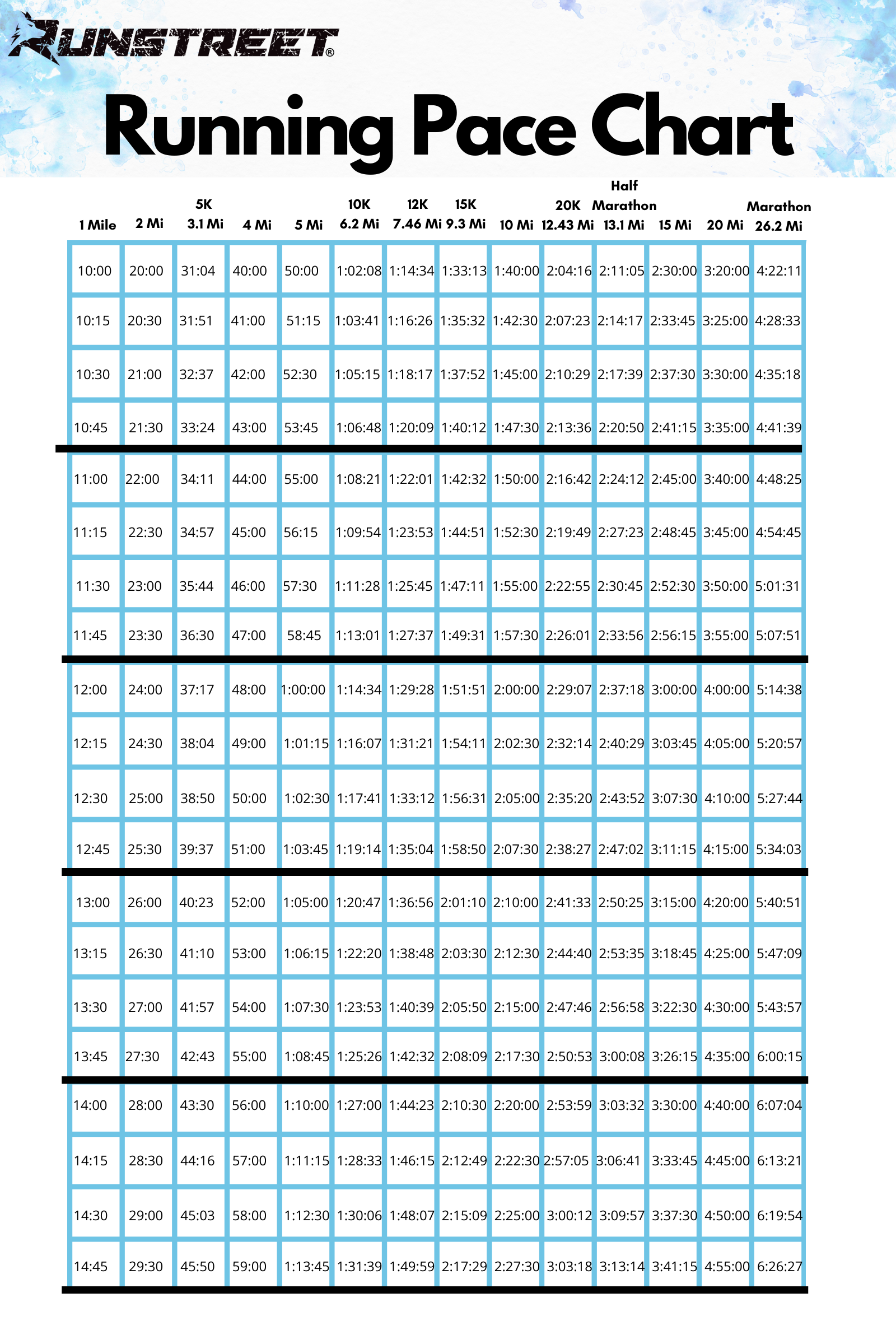






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Demystifying the Running Mile Map: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!