Charting The Crisis: Exploring The Importance Of Mapping Endangered Species
Charting the Crisis: Exploring the Importance of Mapping Endangered Species
Related Articles: Charting the Crisis: Exploring the Importance of Mapping Endangered Species
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Charting the Crisis: Exploring the Importance of Mapping Endangered Species. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Crisis: Exploring the Importance of Mapping Endangered Species

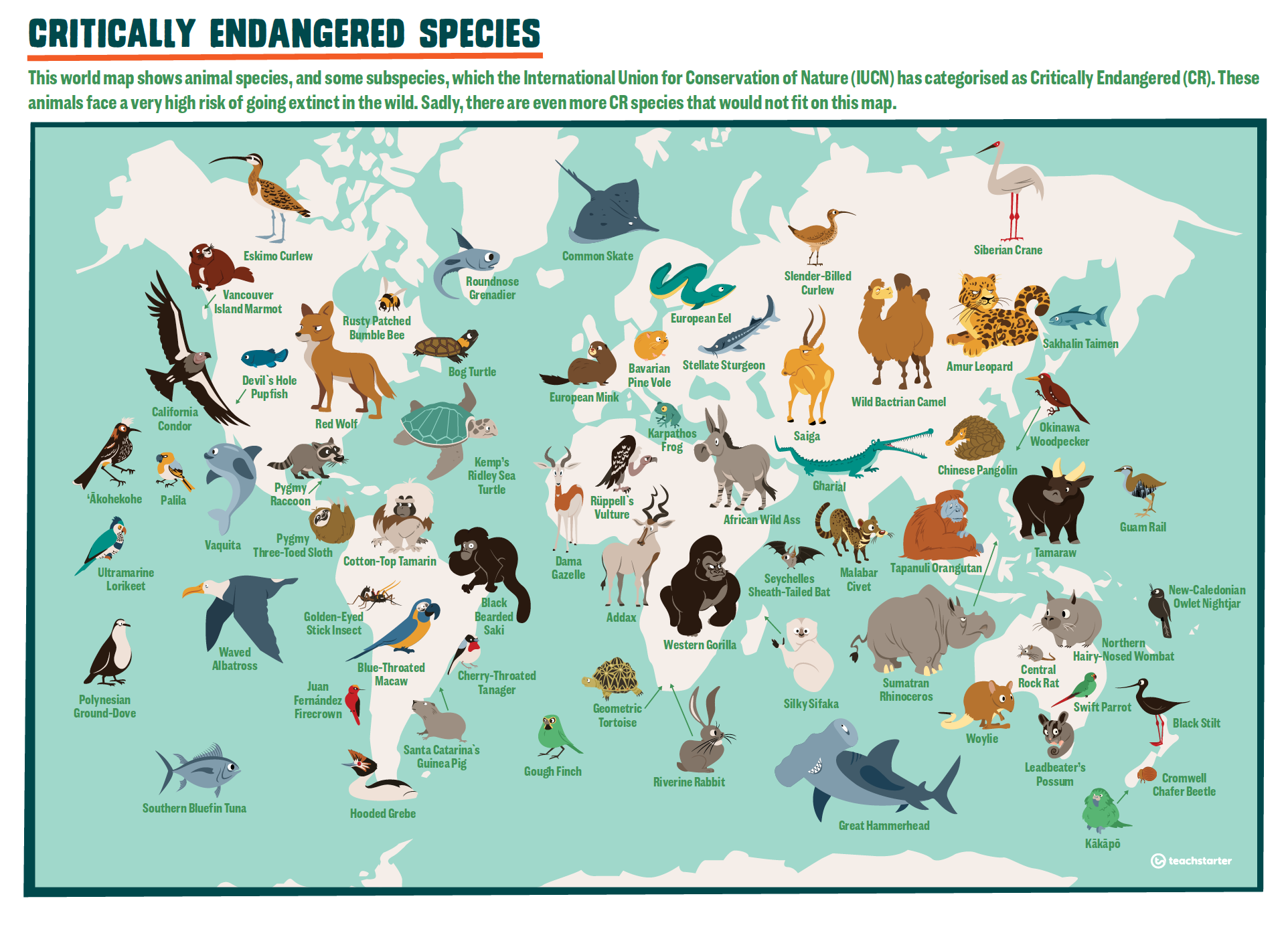
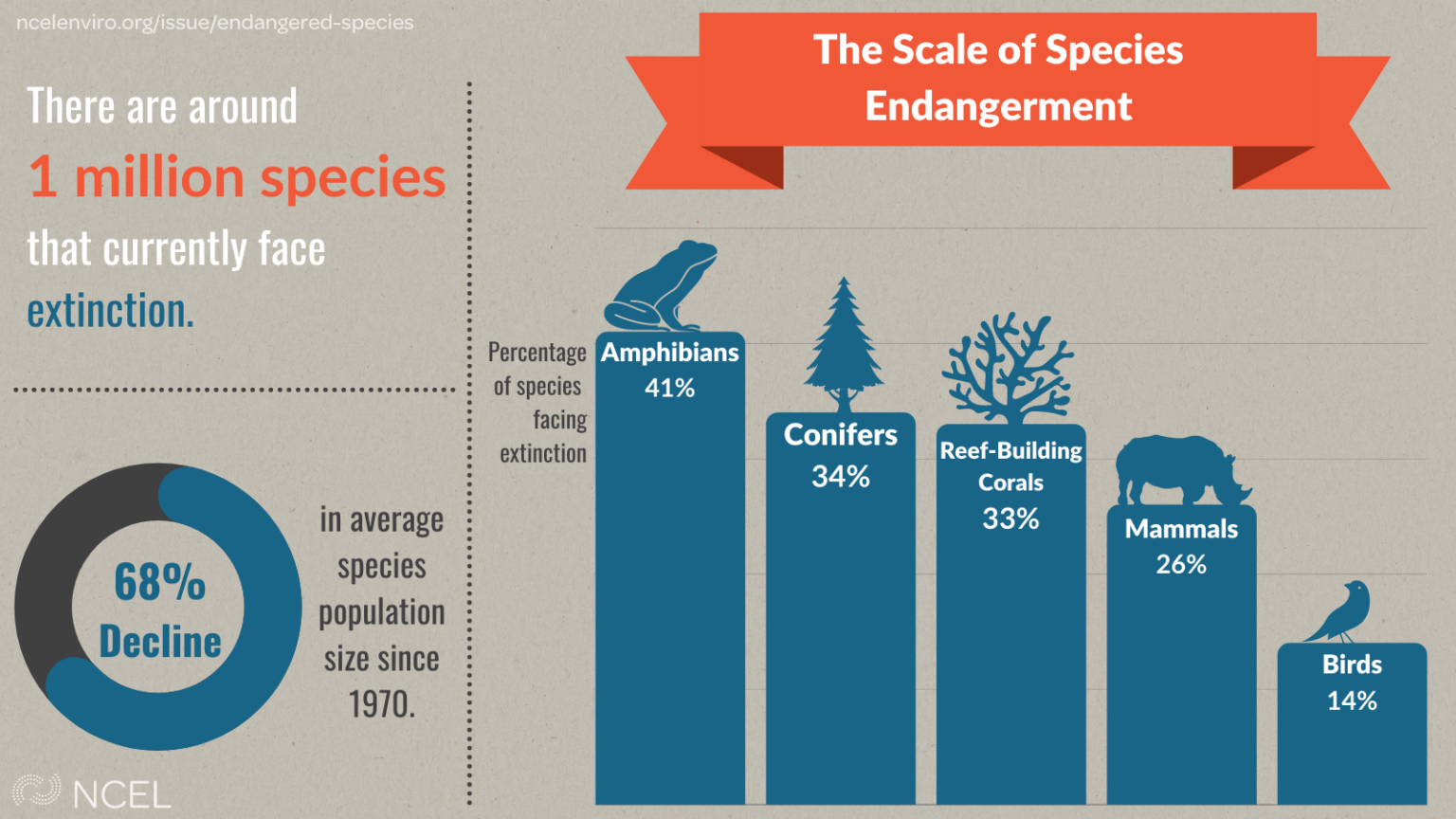
The Earth’s biodiversity is facing an unprecedented crisis. Species are disappearing at an alarming rate, driven by factors like habitat loss, climate change, and unsustainable exploitation. Understanding the distribution and status of threatened species is crucial for effective conservation efforts. This is where the power of mapping endangered species comes into play.
Mapping Endangered Species: A Vital Tool for Conservation
Mapping endangered species provides a visual representation of their geographical distribution, allowing researchers, conservationists, and policymakers to gain valuable insights into their vulnerability and prioritize conservation actions. This process involves:
- Data Collection: Gathering information on species locations, population sizes, habitat types, and threats through surveys, field observations, and citizen science initiatives.
- Spatial Analysis: Utilizing Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to analyze and visualize the collected data, generating maps that illustrate species ranges, population densities, and areas of critical habitat.
- Conservation Planning: Using the generated maps to identify conservation priorities, design protected areas, monitor species populations, and evaluate the effectiveness of conservation efforts.
Benefits of Mapping Endangered Species
Mapping endangered species offers a multitude of benefits, facilitating a comprehensive and data-driven approach to conservation:
- Identifying Hotspots: Maps reveal areas with high concentrations of endangered species, enabling targeted conservation efforts in regions where they are most vulnerable.
- Understanding Distribution: Mapping provides insights into species ranges, population trends, and habitat preferences, helping to understand the factors influencing their decline.
- Prioritizing Conservation Actions: Maps highlight areas of critical habitat, allowing conservationists to focus resources on protecting the most important locations for endangered species survival.
- Monitoring Effectiveness: Maps can track changes in species distribution and population size over time, providing valuable data to evaluate the success of conservation initiatives and adjust strategies as needed.
- Raising Awareness: Visual representations of endangered species distributions effectively communicate the severity of the crisis and engage the public in conservation efforts.
Types of Maps Used for Endangered Species
Various types of maps are employed in endangered species conservation, each serving a specific purpose:
- Species Distribution Maps: Depict the geographical range of a specific species, highlighting areas where it is found and its overall distribution pattern.
- Habitat Suitability Maps: Identify areas that provide suitable conditions for a species to thrive, considering factors like climate, vegetation, and food availability.
- Threat Maps: Visualize the distribution of threats to endangered species, such as habitat loss, pollution, and invasive species, helping to understand the drivers of decline.
- Population Density Maps: Show the concentration of individuals within a species’ range, revealing areas with high population densities that may require targeted conservation efforts.
- Conservation Priority Maps: Combine various data layers to identify areas that are most critical for protecting endangered species, providing a framework for prioritizing conservation resources.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its significant contributions, mapping endangered species faces certain challenges:
- Data Availability: Obtaining accurate and comprehensive data on endangered species can be difficult, especially in remote or understudied regions.
- Species Identification: Distinguishing between similar species and ensuring accurate identification is crucial for reliable mapping, particularly in areas with high biodiversity.
- Dynamic Environments: Species ranges and habitat conditions are constantly changing due to factors like climate change and human activities, requiring ongoing updates and adjustments to mapping efforts.
- Ethical Considerations: Mapping endangered species can increase their vulnerability to poaching and other threats, requiring careful consideration of data sharing and security measures.
Moving Forward: The Future of Mapping Endangered Species
The field of mapping endangered species is continuously evolving with advancements in technology and data analysis techniques. Future trends include:
- Integration of Remote Sensing: Utilizing satellite imagery and aerial photography to monitor species distribution and habitat changes over large areas.
- Citizen Science Initiatives: Engaging the public in data collection through smartphone apps and online platforms to expand the reach and accuracy of species mapping.
- Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence: Employing AI algorithms to analyze vast datasets and predict species distributions, identify threats, and optimize conservation strategies.
- Real-time Monitoring: Developing tools that allow for continuous monitoring of species populations and habitat conditions, providing immediate alerts for potential threats.
FAQs about Mapping Endangered Species
Q: How is mapping endangered species different from mapping other species?
A: Mapping endangered species focuses on species facing a high risk of extinction, requiring a more targeted approach to data collection, analysis, and conservation planning. It prioritizes understanding the specific threats and vulnerabilities of these species to guide effective conservation actions.
Q: What are the limitations of mapping endangered species?
A: Mapping can only be as accurate as the data it uses. Incomplete or inaccurate data can lead to misleading results. Additionally, species ranges and threats are constantly changing, requiring ongoing updates and adjustments to the maps.
Q: How can I get involved in mapping endangered species?
A: Citizen science projects offer opportunities to contribute to data collection and mapping efforts. Several online platforms and apps allow individuals to report species sightings and contribute valuable information to conservation databases.
Q: What are some examples of successful conservation efforts based on endangered species mapping?
A: Mapping has played a vital role in the protection of various endangered species, including the Javan rhinoceros in Indonesia, the mountain gorilla in Central Africa, and the California condor in North America. By identifying critical habitats and monitoring population trends, conservation efforts have been able to effectively protect these species and prevent their extinction.
Tips for Engaging in Endangered Species Mapping
- Support Citizen Science Initiatives: Participate in citizen science projects to contribute to data collection and mapping efforts.
- Learn about Endangered Species in Your Region: Familiarize yourself with the endangered species found in your local area and ways to contribute to their conservation.
- Promote Conservation Awareness: Share information about endangered species and the importance of mapping with your friends, family, and community.
- Support Conservation Organizations: Donate to or volunteer for organizations dedicated to protecting endangered species and their habitats.
Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Protecting Our Planet’s Biodiversity
Mapping endangered species is a powerful tool for understanding the challenges facing our planet’s biodiversity and guiding effective conservation strategies. By combining scientific data with advanced technology, we can gain valuable insights into the distribution, threats, and needs of threatened species, leading to more targeted and impactful conservation actions. As we face an unprecedented biodiversity crisis, embracing the power of mapping endangered species is essential for securing the future of our planet’s unique and irreplaceable wildlife.
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/16218434/Screen_Shot_2019_05_07_at_9.39.50_AM.png)





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Crisis: Exploring the Importance of Mapping Endangered Species. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!