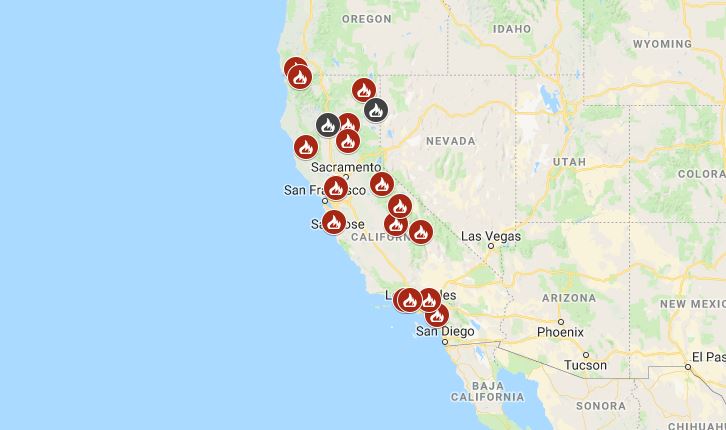
California’s Burning Landscape: A Look Back At The 2018 Fire Season And Its Smoke Map
California’s Burning Landscape: A Look Back at the 2018 Fire Season and Its Smoke Map
Related Articles: California’s Burning Landscape: A Look Back at the 2018 Fire Season and Its Smoke Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to California’s Burning Landscape: A Look Back at the 2018 Fire Season and Its Smoke Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
California’s Burning Landscape: A Look Back at the 2018 Fire Season and Its Smoke Map
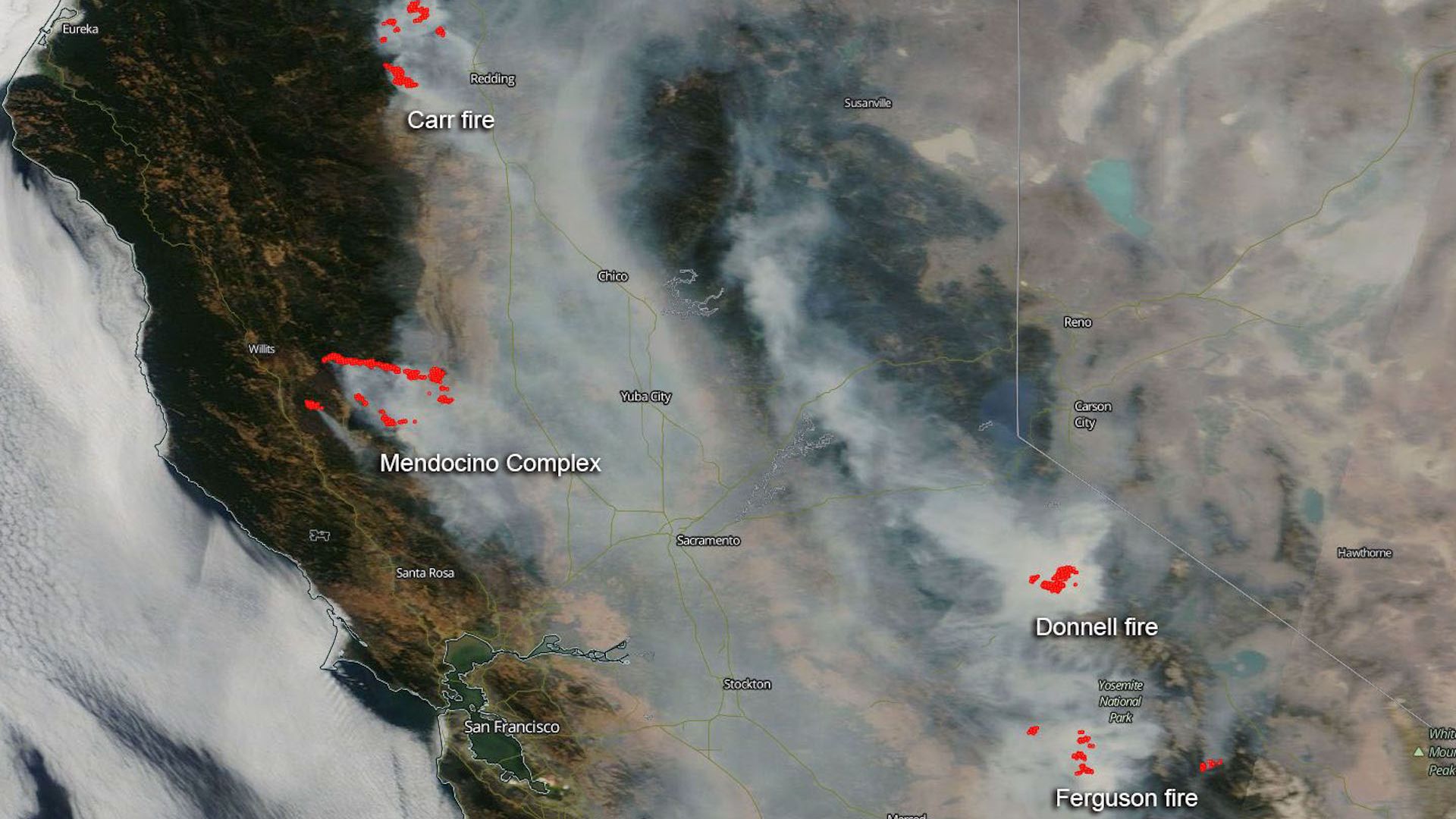
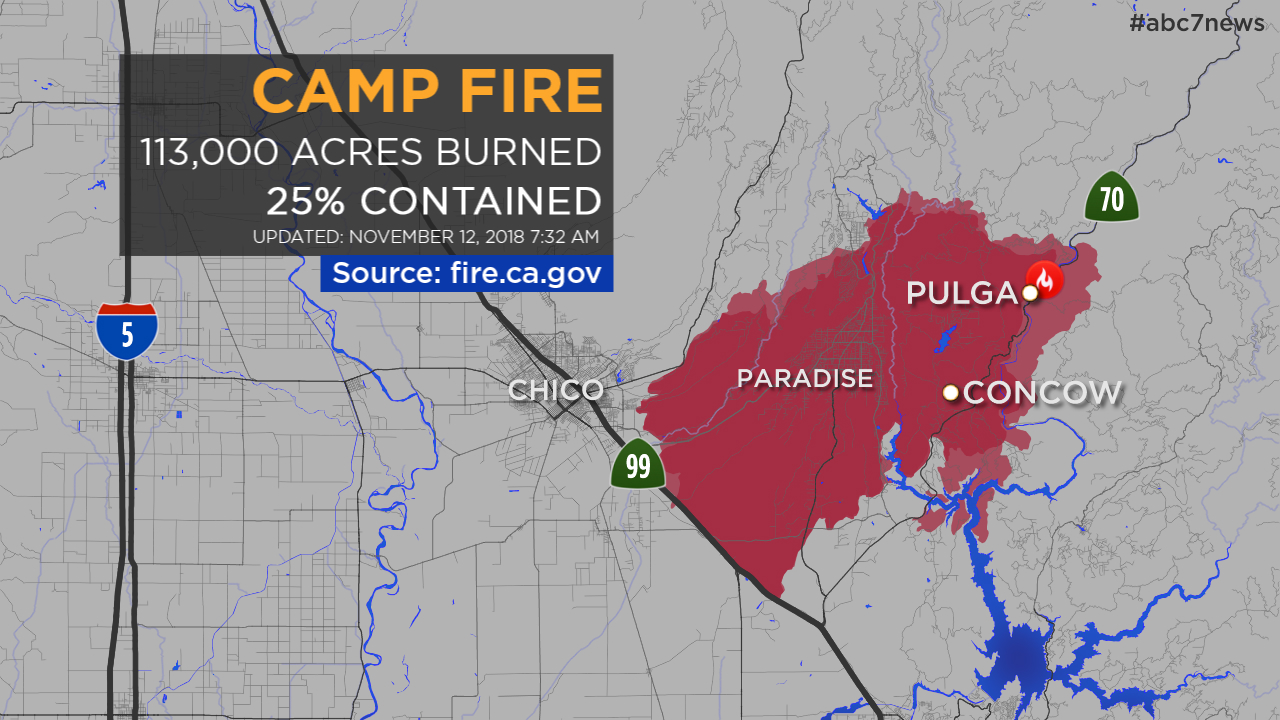
The year 2018 stands as a stark reminder of the increasing severity and impact of wildfires in California. This year witnessed a record-breaking wildfire season, leaving behind a trail of devastation and a lingering cloud of smoke that blanketed the state for months. Understanding the extent and impact of this smoke is crucial for public health, environmental awareness, and disaster preparedness.
The 2018 Fire Season: A Year of Unprecedented Fire Activity
The 2018 wildfire season in California was marked by several factors that contributed to its unprecedented nature:
- Drought Conditions: Prolonged drought conditions had left the state’s vegetation exceptionally dry and susceptible to ignition.
- High Temperatures and Strong Winds: Record-breaking temperatures and strong winds created ideal conditions for the rapid spread of fires.
- Human-Caused Ignition: A significant number of fires were ignited by human activities, highlighting the importance of fire safety measures.
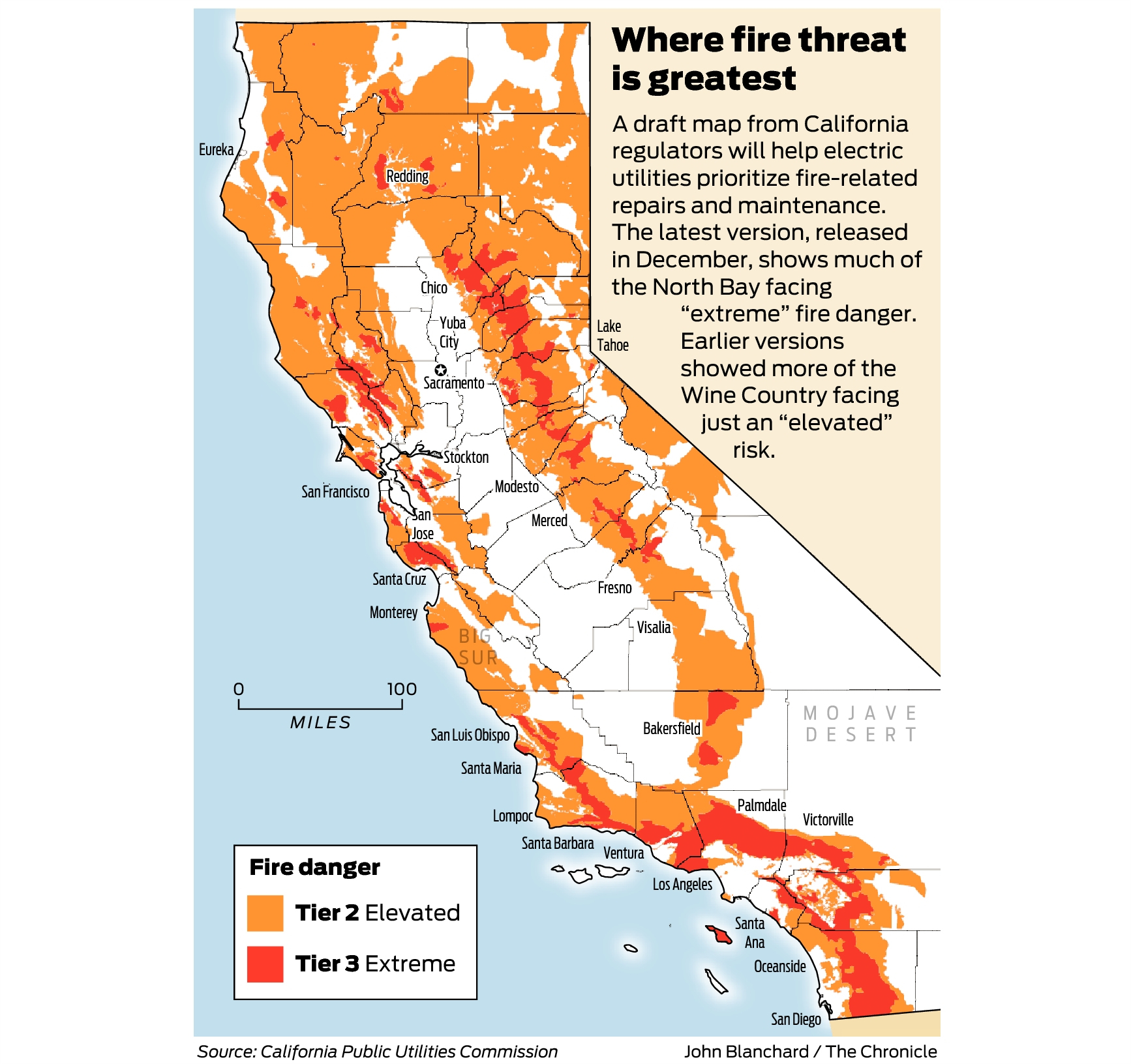
The Smoke Map: A Visual Representation of Air Quality Impact
As wildfires raged across California, the resulting smoke plumes spread across the state and beyond, posing serious threats to public health and air quality. To monitor and understand the impact of this smoke, various organizations utilized real-time data and visualization tools to create smoke maps.
These maps provided a clear and comprehensive picture of the smoke’s movement, concentration, and potential impact on different regions. They were instrumental in:
- Identifying Areas with Elevated Smoke Levels: The maps highlighted areas with high smoke concentrations, allowing authorities to issue air quality alerts and advise residents to take necessary precautions.
- Tracking Smoke Plume Movement: By tracking the movement of smoke plumes, authorities could anticipate areas that would be affected by smoke and issue timely warnings.
- Assessing Health Risks: Smoke maps provided valuable information about the potential health risks associated with smoke exposure, helping healthcare providers and public health agencies to prepare and respond effectively.
The Impact of Smoke on Public Health
Smoke from wildfires contains a complex mixture of pollutants, including particulate matter, carbon monoxide, and volatile organic compounds. Inhalation of these pollutants can have severe health consequences, particularly for vulnerable populations such as children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions.
The health impacts of wildfire smoke can include:
- Respiratory Problems: Smoke can trigger asthma attacks, bronchitis, and other respiratory illnesses.
- Cardiovascular Issues: Exposure to smoke can worsen existing heart conditions and increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Eye and Skin Irritations: Smoke can irritate the eyes, nose, and throat, and can also cause skin rashes.
- Long-Term Health Effects: Chronic exposure to wildfire smoke can lead to long-term health problems, including lung disease and cancer.
Beyond the Immediate Impact: The Environmental Consequences
The environmental consequences of wildfires and their smoke extend beyond immediate health concerns. Smoke can:
- Reduce Air Quality: Wildfire smoke significantly reduces air quality, affecting visibility and impacting ecosystems.
- Damage Vegetation: Smoke can damage vegetation, affecting plant growth and contributing to soil erosion.
- Impact Water Quality: Smoke can contaminate water sources, affecting drinking water quality and aquatic ecosystems.
- Contribute to Climate Change: Wildfires release large amounts of greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change and exacerbating the conditions that fuel future wildfires.
FAQs About the 2018 California Wildfire Smoke Map
Q: What information is typically included on a wildfire smoke map?
A: Wildfire smoke maps typically display:
- Smoke Plume Locations: The location and movement of smoke plumes from active wildfires.
- Smoke Concentration Levels: The concentration of smoke particles in the air, often using color-coded scales.
- Air Quality Index (AQI): The AQI values for different regions, indicating the level of air pollution and associated health risks.
- Wind Direction and Speed: The direction and speed of winds, which influence the movement of smoke plumes.
Q: Where can I find a wildfire smoke map?
A: Wildfire smoke maps are available from various sources, including:
- Government Agencies: The California Air Resources Board (CARB) and the National Weather Service (NWS) provide comprehensive smoke maps.
- Environmental Organizations: Organizations like the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the American Lung Association offer smoke maps and air quality information.
- News Outlets: Many news outlets provide smoke maps and updates on wildfire activity.
Q: How can I use a wildfire smoke map to protect my health?
A: By consulting a smoke map, you can:
- Identify areas with high smoke concentrations: Avoid spending extended periods outdoors in areas with high smoke levels.
- Check the AQI: If the AQI is elevated, limit your outdoor activities and consider wearing a mask.
- Stay Informed: Monitor smoke maps and air quality updates to stay informed about changing conditions.
Tips for Staying Safe During Wildfire Smoke Events
- Reduce Exposure: Limit your time outdoors, especially during periods of high smoke concentration.
- Stay Informed: Monitor air quality reports and smoke maps for updates on smoke levels.
- Use Air Filters: Use HEPA air filters indoors to reduce smoke levels.
- Wear a Mask: Consider wearing a mask when outdoors to reduce smoke inhalation.
- Keep Doors and Windows Closed: Close windows and doors to prevent smoke from entering your home.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to help flush out smoke particles.
- Check on Vulnerable Individuals: Check on elderly neighbors, children, and individuals with respiratory problems.
Conclusion: A Call for Action and Preparedness
The 2018 California wildfire season serves as a stark reminder of the increasing threat posed by wildfires and the importance of understanding their impact. The smoke maps provided valuable insights into the spread and concentration of smoke, allowing authorities and individuals to take proactive measures to protect public health and the environment.
As climate change continues to fuel more frequent and severe wildfires, it is crucial to invest in early detection systems, wildfire prevention strategies, and public awareness campaigns. By understanding the risks and taking necessary precautions, we can mitigate the impact of wildfires and protect our communities from the harmful effects of smoke.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into California’s Burning Landscape: A Look Back at the 2018 Fire Season and Its Smoke Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!