A Comprehensive Guide To The West Virginia District Map: Understanding The Political Landscape
A Comprehensive Guide to the West Virginia District Map: Understanding the Political Landscape
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to the West Virginia District Map: Understanding the Political Landscape
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to the West Virginia District Map: Understanding the Political Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to the West Virginia District Map: Understanding the Political Landscape
- 2 Introduction
- 3 A Comprehensive Guide to the West Virginia District Map: Understanding the Political Landscape
- 3.1 Understanding the Map’s Importance
- 3.2 Historical Context and Evolution of the Map
- 3.3 The 2020 Redistricting Process
- 3.4 Understanding the Current District Map
- 3.5 Navigating the Map: Key Features and Resources
- 3.6 FAQs about the West Virginia District Map
- 3.7 Tips for Understanding and Engaging with the District Map
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
A Comprehensive Guide to the West Virginia District Map: Understanding the Political Landscape
The West Virginia district map is a crucial tool for understanding the state’s political landscape and the representation of its citizens. This map, which is subject to periodic redistricting, defines the boundaries of congressional, state legislative, and county districts. Each district elects a representative to serve in the corresponding legislative body, making the map a vital component of the state’s political system.
Understanding the Map’s Importance
The West Virginia district map serves several key purposes:
- Fair Representation: The map aims to ensure that each district has a roughly equal population, guaranteeing that all citizens have equal voting power. This principle, known as "one person, one vote," is fundamental to democratic representation.
- Community Cohesion: District boundaries are often drawn to keep communities of interest together. This ensures that representatives understand the unique needs and concerns of their constituents.
- Political Accountability: By dividing the state into distinct districts, the map fosters accountability between elected officials and their constituents. Voters can directly hold their representatives responsible for their actions and decisions.
- Election Administration: The map provides clear guidelines for election officials, facilitating the smooth and efficient administration of elections.
Historical Context and Evolution of the Map
The West Virginia district map has undergone significant changes throughout its history. These changes reflect evolving population patterns, demographic shifts, and political considerations.
- Early Redistricting: The initial district map was established when West Virginia became a state in 1863. As the state grew and its population shifted, the map was periodically redrawn to ensure fair representation.
- The Impact of Technology: The advent of computer technology in the late 20th century revolutionized redistricting. Advanced software programs enabled more precise population calculations and allowed for the creation of increasingly complex district boundaries.
- Political Gerrymandering: The process of redistricting has not always been free from political influence. In some instances, political parties have manipulated district boundaries to gain an electoral advantage, a practice known as gerrymandering.
The 2020 Redistricting Process
The 2020 redistricting process in West Virginia was marked by significant challenges. The state’s declining population, coupled with the need to adhere to federal guidelines for equal representation, led to contentious debates and legal challenges.
- Population Shifts: West Virginia experienced a significant population decline in the years leading up to the 2020 census. This decline resulted in the loss of one congressional seat, requiring a redrawing of the state’s congressional districts.
- Federal Guidelines: The Voting Rights Act of 1965, along with other federal legislation, mandates that district boundaries be drawn in a way that does not discriminate against minority voters. This requirement played a key role in the 2020 redistricting process.
- Political Partisanship: The redistricting process was further complicated by partisan politics. Both major political parties sought to draw district boundaries that would favor their candidates in future elections.
Understanding the Current District Map
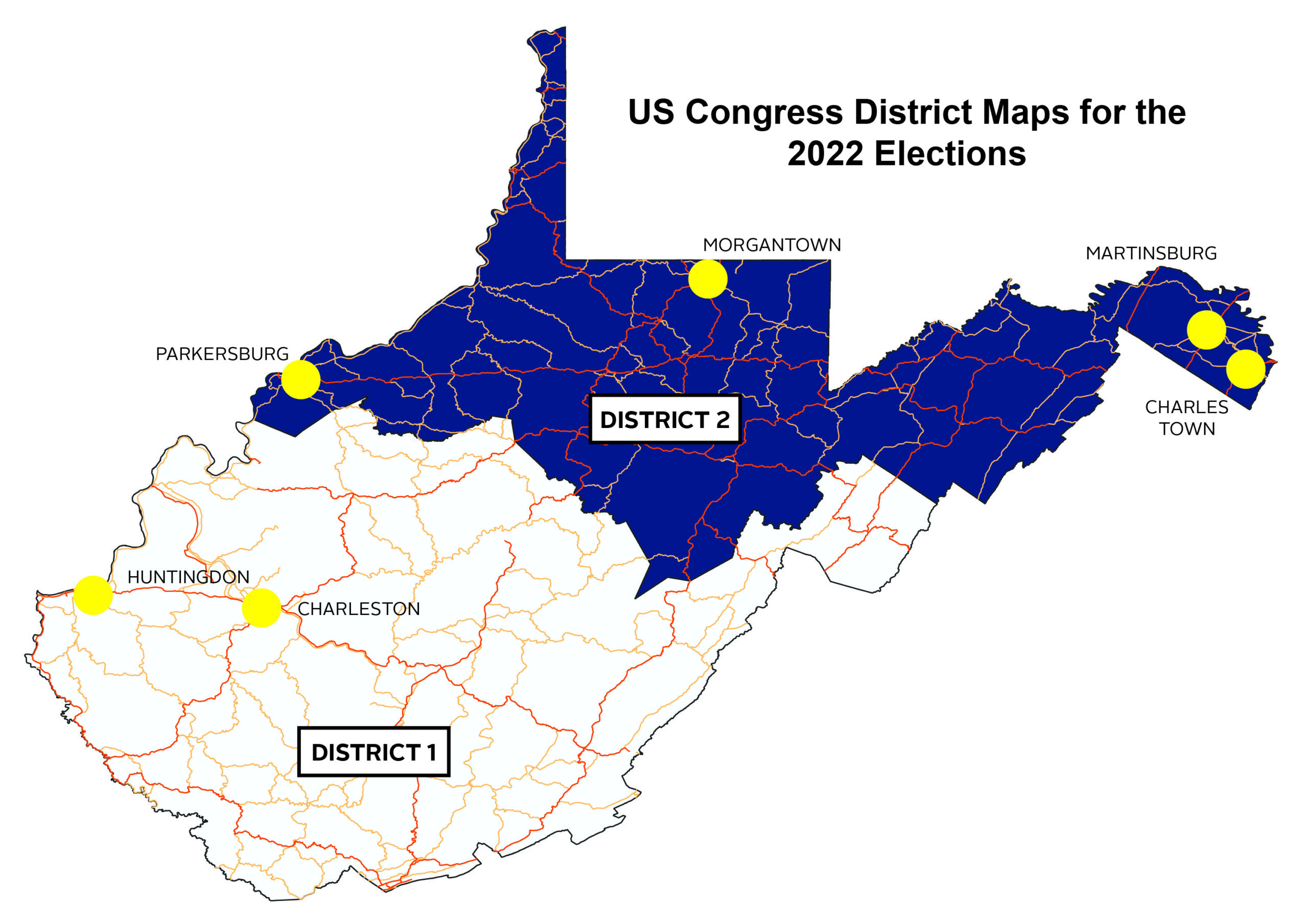
The current West Virginia district map reflects the outcome of the 2020 redistricting process. It divides the state into three congressional districts, 34 state senate districts, and 100 state house districts. Each district is designed to represent a roughly equal population, ensuring fair and equal representation for all citizens.
Navigating the Map: Key Features and Resources
- Online Resources: The West Virginia Secretary of State’s website provides a comprehensive online map of the state’s districts, along with detailed information about each district’s boundaries, population, and elected officials.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software allows users to visualize and analyze spatial data, including district maps. This technology is increasingly being used by researchers, policymakers, and journalists to understand and analyze the implications of district boundaries.
- Public Hearings: The redistricting process typically involves public hearings, where citizens can provide input and express their concerns about proposed district boundaries. These hearings provide an opportunity for the public to engage in the redistricting process and ensure that their interests are considered.
FAQs about the West Virginia District Map
1. How often is the West Virginia district map redrawn?
The West Virginia district map is redrawn every ten years, following the decennial census. This process ensures that districts reflect current population trends and maintain equal representation.
2. Who is responsible for drawing the district boundaries?
In West Virginia, the state legislature is responsible for drawing the district boundaries. This process is typically overseen by a legislative committee.
3. How are district boundaries determined?
District boundaries are determined by a combination of factors, including population, geographic considerations, and community of interest. The goal is to create districts that are as compact and contiguous as possible, while also ensuring equal representation.
4. What is the difference between a congressional district and a state legislative district?
Congressional districts elect representatives to the U.S. House of Representatives, while state legislative districts elect representatives to the state senate and house of delegates. The number of congressional districts in a state is determined by its population, while the number of state legislative districts is determined by state law.
5. How can I find out which district I live in?
You can find out which district you live in by using the online map resources provided by the West Virginia Secretary of State’s office. You can also contact your local election office for assistance.
6. What is the impact of redistricting on elections?
Redistricting can have a significant impact on elections. By drawing district boundaries in a way that favors one party or another, redistricting can influence the outcome of elections and affect the balance of power in the legislature.
7. What are the challenges associated with redistricting?
Redistricting is a complex and often contentious process. Challenges include balancing competing interests, ensuring equal representation, and avoiding political gerrymandering.
Tips for Understanding and Engaging with the District Map
- Stay Informed: Follow news coverage and attend public hearings to stay informed about the redistricting process and the proposed district boundaries.
- Engage in Dialogue: Participate in community discussions and share your perspectives on redistricting with your elected officials.
- Support Fair Redistricting: Advocate for fair and impartial redistricting processes that prioritize equal representation and community cohesion.
- Educate Yourself: Learn about the history and principles of redistricting, as well as the impact it has on elections and representation.
Conclusion
The West Virginia district map is a fundamental component of the state’s political system, shaping the representation of its citizens and influencing the outcome of elections. Understanding the map’s importance, its historical context, and the current redistricting process is crucial for engaging in informed political discourse and ensuring fair and equitable representation for all West Virginians. By staying informed, participating in public dialogue, and advocating for fair redistricting practices, citizens can play a vital role in shaping the state’s political landscape and ensuring that their voices are heard.
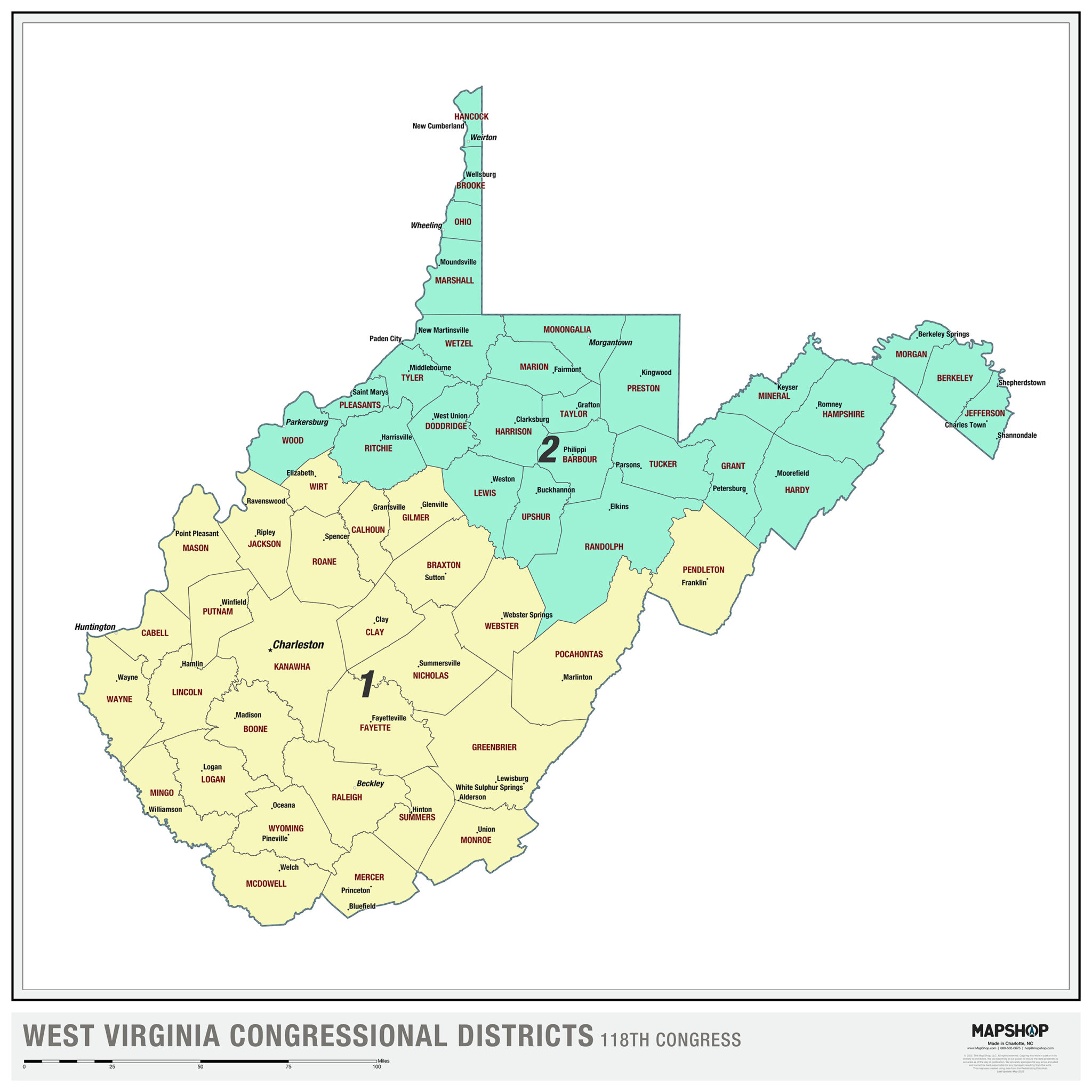




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to the West Virginia District Map: Understanding the Political Landscape. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!